Melanoma induces immunosuppression by up-regulating FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells
- PMID: 17574040
- PMCID: PMC2043471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.03.053
Melanoma induces immunosuppression by up-regulating FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells
Abstract
Background: The immune response to melanoma is rarely curative, suggesting the emergence of immunosuppression. FOXP3-expressing regulatory T cells (T(reg) cells) function to suppress immune responses. The objective of this study was to determine if melanoma evades immune surveillance, in part, by inducing T(reg) cells.
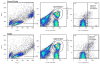
Material and methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and exposed to melanoma-conditioned media (MCM) or control media for 1 week. The induction of T(reg) cells in these PBMCs was determined by measuring the proportion of CD25(+)FOXP3(+) T cells in all CD4(+) T cells by flow cytometry. FOXP3 expression was determined by mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) and Western blot. Supernatant cytokines were determined by ELISA.
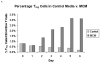
Results: Normal PBMCs exposed to MCM revealed higher proportions of T(reg) cells than those exposed to control media after 6 days (3.4% versus 1.3%, respectively, P < 0.02). The expression of FOXP3 in T(reg) cells from PBMCs exposed to MCM increased over time by MFI and Western blot but was not significantly different than those exposed to control media. The level of IL-10 and TGF-beta in supernatants after 6 days growth was higher in MCM than control media, but this did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion: Exposure of PBMCs to melanoma results in induction of FOXP3(+) T(reg) cells.
Figures


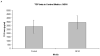
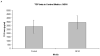
References
-
- Manola J, Atkins M, Ibrahim J, Kirkwood J. Prognostic factors in metastatic melanoma: a pooled analysis of Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trials. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:3782–3793. - PubMed
-
- Saleh F, Renno W, Klepacek I, Ibrahim G, Dashti H, Asfar S, Behbehani A, Al-Sayer H, Dashti A. Direct evidence on the immune-mediated spontaneous regression of human cancer: an incentive for pharmaceutical companies to develop a novel anti-cancer vaccine. Current pharmaceutical design. 2005;11:3531–3543. - PubMed
-
- Jack A, Boyes C, Aydin N, Alam K, Wallack M. The treatment of melanoma with an emphasis on immunotherapeutic strategies. Surgical oncology. 2006;15:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Lotze MT, Chang AE, Seipp CA, Simpson C, Vetto JT, Rosenberg SA. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 in the treatment of patients with disseminated cancer. Responses, treatment-related morbidity, and histologic findings. Jama. 1986;256:3117–3124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

