Effects of doxazosin on blood flow and mRNA expression of nitric oxide synthase in the spontaneously hypertensive rat genitourinary tract
- PMID: 17574276
- PMCID: PMC2077832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.05.004
Effects of doxazosin on blood flow and mRNA expression of nitric oxide synthase in the spontaneously hypertensive rat genitourinary tract
Abstract
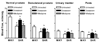
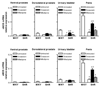
Hypertension may impact pelvic arterial blood flow resulting in reduction of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) levels. Although doxazosin, an alpha(1)-adrenoceptor antagonist, has been shown to improve erectile dysfunction as well as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and hypertension, it is not clear whether these improvements using doxazosin are primarily due to direct actions on the prostate, urinary bladder and penis, possibly via inhibition of vascular alpha(1)-adrenoceptors, or other sites of actions. Therefore, we investigated effects of doxazosin to the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) on blood flow and NOS levels in the genitourinary tract. Four groups of rats were assessed: group 1, SHRs treated with doxazosin (30 mg/kg/day) for 4 weeks; group 2, SHRs treated with nifedipine (30 mg/kg/day) for 4 weeks; group 3, untreated SHRs; and group 4, untreated Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats. Blood flow to the ventral prostate, dorsolateral prostate, urinary bladder and penis was determined using a fluorescent microsphere infusion technique. Expression levels of nNOS and eNOS mRNAs were quantified by real-time RT-PCR using SYBR Green I. Blood flow to the ventral prostate, dorsolateral prostate, urinary bladder and penis was significantly lower in untreated SHRs than WKY rats. Treatment with doxazosin increased blood flow to each tissue studied in SHRs. RT-PCR data indicated that untreated SHRs had lower mRNA expression levels of nNOS in the bladder and penis and eNOS in the penis than WKY rats and that administration of doxazosin to the SHR caused an increase in expression levels of these genes, i.e., up-regulation of nNOS in the bladder and penis and eNOS in the penis. However, nifedipine had no significant effects on blood flow and NOS levels in the SHR genitourinary tract. Our data demonstrate that doxazosin treatment causes differential alterations in blood flow and NOS levels in the SHR genitourinary tract. These findings may provide insight into the beneficial effects of alpha(1)-adrenoceptor antagonists, on prostate, bladder and penile function, when used to treat symptoms of BPH and elevated blood pressure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential effects of prazosin and naftopidil on pelvic blood flow and nitric oxide synthase levels in spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2008;28(4):403-12. doi: 10.1080/10799890802176626. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2008. PMID: 18702011
-
Molecular mechanisms regulating urogenital expression of nitric oxide synthase in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Life Sci. 2009 Aug 12;85(7-8):334-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.06.014. Epub 2009 Jul 2. Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19576905
-
Identification of potential therapeutic targets in hypertension-associated bladder dysfunction.BJU Int. 2010 Mar;105(6):877-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08809.x. Epub 2009 Aug 18. BJU Int. 2010. PMID: 19689474
-
The spontaneously hypertensive rat: insight into the pathogenesis of irritative symptoms in benign prostatic hyperplasia and young anxious males.Exp Physiol. 1999 Jan;84(1):137-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-445x.1999.tb00079.x. Exp Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10081714 Review.
-
After ALLHAT: doxazosin for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 Sep;5(9):1957-64. doi: 10.1517/14656566.5.9.1957. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15330733 Review.
Cited by
-
Are blood vessels a target to treat lower urinary tract dysfunction?Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;388(7):687-94. doi: 10.1007/s00210-015-1137-y. Epub 2015 May 31. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26026700
-
New Frontiers of Basic Science Research in Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction.Urol Clin North Am. 2017 Aug;44(3):491-505. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2017.04.014. Urol Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28716328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Knowledge and Novel Frontiers in Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction after Spinal Cord Injury: Basic Research Perspectives.Urol Sci. 2022 Jul-Sep;33(3):101-113. doi: 10.4103/uros.uros_31_22. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Urol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36177249 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the associative role of hypertension and angiotensin II receptor in lower urinary tract dysfunction.Hypertens Res. 2024 Apr;47(4):987-997. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01597-8. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38351189 Review.
-
Metabolic syndrome and urologic diseases.Rev Urol. 2010 Fall;12(4):e157-80. Rev Urol. 2010. PMID: 21234260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Major cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients randomized to doxazosin vs chlorthalidone: the antihypertensive and lipid-lowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial (ALLHAT) Journal of the American Medical Association. 2000;283(15):1967–1975. - PubMed
-
- Burnett AL. Nitric oxide control of lower genitourinary tract functions: a review. Urology. 1995;45(6):1071–1083. - PubMed
-
- Choppin A, Blue DR, Hegde SS, Gennevois D, McKinnon SA, Mokatrin A, Bivalacqua TJ, Hellstrom WJ. Evaluation of oral Ro70-0004/003, an α1A-adrenoceptor antagonist, in the treatment of male erectile dysfunction. International Journal of Impotence Research. 2001;13(3):157–161. - PubMed
-
- Das AK, Leggett RE, Whitbeck C, Eagen G, Levin RM. Effect of doxazosin on rat urinary bladder function after partial outlet obstruction. Neurourology and Urodynamics. 2002;21(2):160–166. - PubMed
-
- Foster HE, Jr, Yono M, Shin D, Takahashi W, Pouresmail M, Afiatpour P, Latifpour J. Effects of chronic administration of doxazosin on α1-adrenoceptors in the rat prostate. Journal of Urology. 2004;172(6 Pt 1):2465–2470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

