Effects of epidermal growth factor on atrophic enteritis in piglets induced by experimental porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus
- PMID: 17574457
- PMCID: PMC7129753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.04.018
Effects of epidermal growth factor on atrophic enteritis in piglets induced by experimental porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus
Abstract
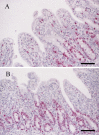
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) promotes gastrointestinal mucosal recovery by stimulating the mitogenic activity of intestinal crypt epithelial cells. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of EGF on atrophic enteritis induced in piglets by experimental infection with porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) strain Dr13. Two groups of 12 conventional, colostrum-deprived, 1-day-old, large White-Duroc cross breed piglets were inoculated orally with PEDV (3 x 10(5) 50% tissue culture infective doses), with or without EGF (10 microg/kg/day, intraperitoneally once daily for 4 days after infection) and compared to 12 uninfected, untreated control piglets. PEDV+EGF piglets had less severe clinical signs than PEDV only piglets at 48 and 60 h post-infection (hpi). Histologically, the ratio of villous height:crypt depth of PEDV+EGF piglets was significantly higher than PEDV only piglets at 36 and 48 hpi. Immunohistochemistry for Ki67 demonstrated increased proliferation in intestinal crypt epithelial cells of PEDV+EGF piglets compared to PEDV only piglets at 36, 48 and 60 hpi. EGF stimulates proliferation of intestinal crypt epithelial cells and promotes recovery from atrophic enteritis in PEDV-infected piglets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection: Etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis and immunoprophylaxis.Vet J. 2015 May;204(2):134-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Vet J. 2015. PMID: 25841898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative pathogenesis of US porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) strain PC21A in conventional 9-day-old nursing piglets vs. 26-day-old weaned pigs.Vet Microbiol. 2015 Jul 9;178(1-2):31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Vet Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25939885 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of transplacental porcine circovirus type 2 infection on porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus-induced enteritis in preweaning piglets.Vet J. 2006 May;171(3):445-50. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2005.02.016. Vet J. 2006. PMID: 16624710 Free PMC article.
-
Structural alteration of tight and adherens junctions in villous and crypt epithelium of the small and large intestine of conventional nursing piglets infected with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus.Vet Microbiol. 2015 Jun 12;177(3-4):373-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.03.022. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Vet Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25843943 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine deltacoronavirus infection: Etiology, cell culture for virus isolation and propagation, molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2016 Dec 2;226:50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.04.009. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27086031 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Communication: The relationship of enterocyte proliferation with intestinal morphology and nutrient digestibility in weaning piglets.J Anim Sci. 2019 Jan 1;97(1):353-358. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky388. J Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 30304539 Free PMC article.
-
Fermented Soybean Meal Affects the Reproductive Performance and Oxidative Status of Sows, and the Growth of Piglets.Animals (Basel). 2021 Feb 24;11(3):597. doi: 10.3390/ani11030597. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668322 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative and kinetic analysis of viral shedding and immunological responses in MERS patients representing a broad spectrum of disease severity.Sci Rep. 2016 May 5;6:25359. doi: 10.1038/srep25359. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27146253 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus: a comprehensive review of molecular epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccines.Virus Genes. 2012 Apr;44(2):167-75. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0713-1. Epub 2012 Jan 22. Virus Genes. 2012. PMID: 22270324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection: Etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis and immunoprophylaxis.Vet J. 2015 May;204(2):134-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Vet J. 2015. PMID: 25841898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barnard J.A., Beauchamp R.D., Russell W.E., Dubois R.N., Coffey R.J. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their relevance to gastrointestinal pathophysiology. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:564–580. - PubMed
-
- Chae C., Kim O., Choi C., Min K., Cho W.-S., Kim J., Tai J.H. Prevalence of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and transmissible gastroenteritis virus infection in Korean pigs. Veterinary Record. 2000;147:606–608. - PubMed
-
- Danilenko D.M., Ring B.D., Tarpley J.E., Morris B., Van G.Y., Morawiecki A., Callahan W., Goldenberg M., Hershenson S., Pierce G.F. Differing targets and effects of keratinocyte growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor-BB, epidermal growth factor, and neu differentiation factor. American Journal of Pathology. 1995;147:1261–1277. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dorr W., Bassler S., Reichel S., Spekl K. Reduction of radiochemotherapy-induced early oral mucositis by recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor (palifermin): experimental studies in mice. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology and Physics. 2005;62:881–887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

