RACK1 regulates Src activity and modulates paxillin dynamics during cell migration
- PMID: 17574549
- PMCID: PMC2679865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.05.013
RACK1 regulates Src activity and modulates paxillin dynamics during cell migration
Abstract
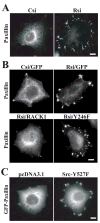
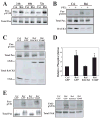
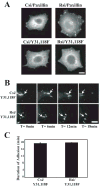
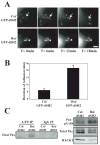
Receptor for Activated C Kinase, RACK1, is an adaptor protein that regulates signaling via Src and PKC-dependent pathways, and has been implicated in cell migration. In this study we demonstrate novel functions for RACK1 in regulating adhesion dynamics during cell migration. We report that cells lacking RACK1 are less motile and show reduced dynamics of paxillin and talin at focal complexes. To investigate the role of the RACK1/Src interactions in adhesion dynamics, we used RACK1 in which the putative Src binding site has been mutated (RACK Y246F). RACK1-deficient cells showed enhanced c-Src activity that was rescued by expression of wild type RACK1, but not by RACK Y246F. Expression of wild type RACK1, but not RACK Y246F, was also able to rescue the adhesion and migration defects observed in the RACK1-deficient cells. Furthermore, our findings indicate that RACK1 functions to regulate paxillin phosphorylation and that its effects on paxillin dynamics require the Src-mediated phosphorylation of tyrosine 31/118 on paxillin. Taken together, these findings support a novel role for RACK1 as a key regulator of cell migration and adhesion dynamics through the regulation of Src activity, and the modulation of paxillin phosphorylation at early adhesions.
Figures
References
-
- Jockusch BM, Bubeck P, Giehl K, Kroemker M, Moschner J, Rothkegel M, Rudiger M, Schluter K, Stanke G, Winkler J. The molecular architecture of focal adhesions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:379–416. - PubMed
-
- Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110:673–87. - PubMed
-
- Burridge K, Fath K, Kelly T, Nuckolls G, Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz MA, Schaller MD, Ginsberg MH. Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:549–99. - PubMed
-
- Ilic D, Furuta Y, Kanazawa S, Takeda N, Sobue K, Nakatsuji N, Nomura S, Fujimoto J, Okada M, Yamamoto T. Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature. 1995;377:539–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

