Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1-infected cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukaemia cells
- PMID: 17576198
- PMCID: PMC1948965
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070286
Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1-infected cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukaemia cells
Retraction in
-
Retraction. Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1-infected cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukaemia cells.Biochem J. 2011 Mar 15;434(3):571. doi: 10.1042/bj4340571. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21348857 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
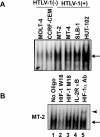
HTLV-1 (human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1) is the causative agent for ATL (adult T-cell leukaemia). HTLV-1 Tax can activate the PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase)/Akt signalling pathway, which is responsible for survival of HTLV-1-infected T-cells. HIFs (hypoxia-inducible factors) are transcriptional regulators that play a central role in the response to hypoxia. Overexpression of HIF-1alpha in many cancers is associated with a poor response to treatment and increased patient mortality. Our objectives in the present study were to investigate whether HIF-1 was activated in HTLV-1-infected T-cells and to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of HIF-1 activation by focusing on the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. We detected a potent pathway that activated HIF-1 in the HTLV-1-infected T-cells under a normal oxygen concentration. Enhanced HIF-1alpha protein expression and HIF-1 DNA-binding activity were exhibited in HTLV-1-infected T-cell lines. Knockdown of HIF-1alpha by siRNA (small interfering RNA) suppressed the growth and VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) expression of the HTLV-1-infected T-cell line. HIF-1 protein accumulation and transcriptional activity were enhanced by Tax, which was inhibited by dominant-negative Akt. Importantly, mutant forms of Tax that are defective in activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway failed to induce HIF-1 transcriptional activity. The PI3K inhibitor LY294002 suppressed HIF-1alpha protein expression, HIF-1 DNA-binding and HIF-1 transcriptional activity in HTLV-1-infected T-cell lines. In primary ATL cells, HIF-1alpha protein levels were strongly correlated with levels of phosphorylated Akt. The results of the present study suggest that PI3K/Akt activation induced by Tax leads to activation of HIF-1. As HIF-1 plays a major role in tumour progression, it may represent a molecular target for the development of novel ATL therapeutics.
Figures


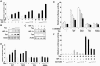
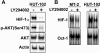

Similar articles
-
4-Hydroxy estradiol but not 2-hydroxy estradiol induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor A through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/FRAP pathway in OVCAR-3 and A2780-CP70 human ovarian carcinoma cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004 Apr 1;196(1):124-35. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2003.12.002. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15050414
-
YC-1 inhibits HIF-1 expression in prostate cancer cells: contribution of Akt/NF-kappaB signaling to HIF-1alpha accumulation during hypoxia.Oncogene. 2007 Jun 7;26(27):3941-51. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210169. Epub 2007 Jan 8. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17213816
-
Silibinin inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1 signalling pathway in human cervical and hepatoma cancer cells: implications for anticancer therapy.Oncogene. 2009 Jan 22;28(3):313-24. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.398. Epub 2008 Nov 3. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 18978810
-
The Mechanism of Trivalent Inorganic Arsenic on HIF-1α: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020 Dec;198(2):449-463. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02087-x. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020. PMID: 32124230
-
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a by reactive oxygen species: new developments in an old debate.J Cell Biochem. 2015 May;116(5):696-703. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25074. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25546605 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential gene expression analysis in k562 human leukemia cell line treated with benzene.Toxicol Res. 2011 Mar;27(1):43-8. doi: 10.5487/TR.2011.27.1.043. Toxicol Res. 2011. PMID: 24278550 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1 Tax deregulates autophagy by recruiting autophagic molecules into lipid raft microdomains.Oncogene. 2015 Jan 15;34(3):334-45. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.552. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24362528 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the oxidative stress pathway by HIV-1 Vpr leads to induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression.J Biol Chem. 2009 Apr 24;284(17):11364-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809266200. Epub 2009 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19204000 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.Oncogene. 2010 Feb 4;29(5):625-34. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.441. Epub 2009 Nov 30. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 19946328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microscale electroporation: challenges and perspectives for clinical applications.Integr Biol (Camb). 2009 Mar;1(3):242-51. doi: 10.1039/b819201d. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Integr Biol (Camb). 2009. PMID: 20023735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tajima K. The 4th nation-wide study of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) in Japan: estimates of risk of ATL and its geographical and clinical features. The T- and B-cell Malignancy Study Group. Int. J. Cancer. 1990;45:237–243. - PubMed
-
- Yamada Y., Tomonaga M., Fukuda H., Hanada S., Utsunomiya A., Tara M., Sano M., Ikeda S., Takatsuki K., Kozuru M., et al. A new G-CSF-supported combination chemotherapy, LSG15, for adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study 9303. Br. J. Haematol. 2001;113:375–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

