BACE1 regulates voltage-gated sodium channels and neuronal activity
- PMID: 17576410
- PMCID: PMC2747787
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1602
BACE1 regulates voltage-gated sodium channels and neuronal activity
Abstract
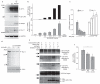
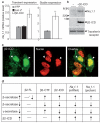
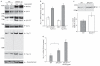
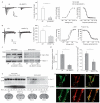
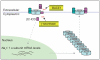
BACE1 activity is significantly increased in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients, potentially contributing to neurodegeneration. The voltage-gated sodium channel (Na(v)1) beta2-subunit (beta2), a type I membrane protein that covalently binds to Na(v)1 alpha-subunits, is a substrate for BACE1 and gamma-secretase. Here, we find that BACE1-gamma-secretase cleavages release the intracellular domain of beta2, which increases mRNA and protein levels of the pore-forming Na(v)1.1 alpha-subunit in neuroblastoma cells. Similarly, endogenous beta2 processing and Na(v)1.1 protein levels are elevated in brains of BACE1-transgenic mice and Alzheimer's disease patients with high BACE1 levels. However, Na(v)1.1 is retained inside the cells and cell surface expression of the Na(v)1 alpha-subunits and sodium current densities are markedly reduced in both neuroblastoma cells and adult hippocampal neurons from BACE1-transgenic mice. BACE1, by cleaving beta2, thus regulates Na(v)1 alpha-subunit levels and controls cell-surface sodium current densities. BACE1 inhibitors may normalize membrane excitability in Alzheimer's disease patients with elevated BACE1 activity.
Figures

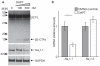
References
-
- Assal F, Cummings JL. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in the dementias. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2002;15:445–450. - PubMed
-
- Mendez M, Lim G. Seizures in elderly patients with dementia: epidemiology and management. Drugs Aging. 2003;20:791–803. - PubMed
-
- Hesdorffer DC, Hauser WA, Annegers JF, Kokmen E, Rocca WA. Dementia and adult-onset unprovoked seizures. Neurology. 1996;46:727–730. - PubMed
-
- Hauser WA, Morris ML, Heston LL, Anderson VE. Seizures and myoclonus in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1986;36:1226–1230. - PubMed
-
- Larner AJ, Doran M. Clinical phenotypic heterogeneity of Alzheimer’s disease associated with mutations of the presenilin-1 gene. J. Neurol. 2006;253:139–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

