oPOSSUM: integrated tools for analysis of regulatory motif over-representation
- PMID: 17576675
- PMCID: PMC1933229
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm427
oPOSSUM: integrated tools for analysis of regulatory motif over-representation
Abstract
The identification of over-represented transcription factor binding sites from sets of co-expressed genes provides insights into the mechanisms of regulation for diverse biological contexts. oPOSSUM, an internet-based system for such studies of regulation, has been improved and expanded in this new release. New features include a worm-specific version for investigating binding sites conserved between Caenorhabditis elegans and C. briggsae, as well as a yeast-specific version for the analysis of co-expressed sets of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes. The human and mouse applications feature improvements in ortholog mapping, sequence alignments and the delineation of multiple alternative promoters. oPOSSUM2, introduced for the analysis of over-represented combinations of motifs in human and mouse genes, has been integrated with the original oPOSSUM system. Analysis using user-defined background gene sets is now supported. The transcription factor binding site models have been updated to include new profiles from the JASPAR database. oPOSSUM is available at http://www.cisreg.ca/oPOSSUM/
Figures
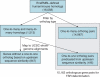

References
-
- Huang SS, Fulton DL, Arenillas DJ, Perco P, Ho Sui SJ, Mortimer JR, Wasserman WW. Advances in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. Vol. 3. London, UK: Imperial College Press; 2006. Identification of over-represented combinations of transcription factor binding sites in sets of co-expressed genes; pp. 247–256.
-
- Urnov FD, Rebar EJ. Designed transcription factors as tools for therapeutics and functional genomics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002;64:919–923. - PubMed
-
- Sandelin A, Wasserman WW. Constrained binding site diversity within families of transcription factors enhances pattern discovery bioinformatics. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;338:207–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

