Double knockouts reveal that protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B is a physiological target of calpain-1 in platelets
- PMID: 17576811
- PMCID: PMC1952154
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00522-07
Double knockouts reveal that protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B is a physiological target of calpain-1 in platelets
Abstract
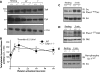
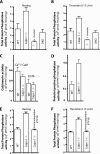
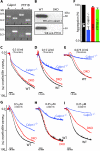
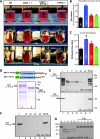
Calpains are ubiquitous calcium-regulated cysteine proteases that have been implicated in cytoskeletal organization, cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell motility, and hemostasis. Gene targeting was used to evaluate the physiological function of mouse calpain-1 and establish that its inactivation results in reduced platelet aggregation and clot retraction potentially by causing dephosphorylation of platelet proteins. Here, we report that calpain-1 null (Capn1-/-) platelets accumulate protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), which correlates with enhanced tyrosine phosphatase activity and dephosphorylation of multiple substrates. Treatment of Capn1-/- platelets with bis(N,N-dimethylhydroxamido)hydroxooxovanadate, an inhibitor of tyrosine phosphatases, corrected the aggregation defect and recovered impaired clot retraction. More importantly, platelet aggregation, clot retraction, and tyrosine dephosphorylation defects were rescued in the double knockout mice lacking both calpain-1 and PTP1B. Further evaluation of mutant mice by the ferric chloride-induced arterial injury model suggests that the Capn1-/- mice are relatively resistant to thrombosis in vivo. Together, our results demonstrate that PTP1B is a physiological target of calpain-1 and suggest that a similar mechanism may regulate calpain-1-mediated tyrosine dephosphorylation in other cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Calpain-mediated regulation of platelet signaling pathways.Curr Opin Hematol. 2007 May;14(3):249-54. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3280ef68f8. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17414215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of the mouse mu-calpain gene reveals an essential role in platelet function.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Mar;21(6):2213-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.6.2213-2220.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238954 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted gene inactivation reveals a functional role of calpain-1 in platelet spreading.J Thromb Haemost. 2012 Jun;10(6):1120-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04715.x. J Thromb Haemost. 2012. PMID: 22458296 Free PMC article.
-
Participation of calpain in protein-tyrosine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in human blood platelets.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):511-4. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.4.511. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995. PMID: 7749863
-
All cut up! The consequences of calpain activation on platelet function.Vascul Pharmacol. 2012 May-Jun;56(5-6):210-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Vascul Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22386643 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid degradation of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B in sickle cells: Possible contribution to sickle cell membrane weakening.FASEB J. 2022 Jun;36(6):e22360. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100809RR. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35593742 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species play a critical role in collagen-induced platelet activation via SHP-2 oxidation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Jun 1;20(16):2528-40. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5337. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24093153 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of platelet-activating factor-mediated protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B activation by a Janus kinase 2/calpain pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 7;12(7):e0180336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180336. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28686728 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain-1 inhibition attenuates in vivo thrombosis in a humanized model of sickle cell disease.Thromb Res. 2022 Mar;211:123-126. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2022.01.029. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Thromb Res. 2022. PMID: 35149397 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Targeting Tyrosine Phosphatases by 3-Bromopyruvate Overcomes Hyperactivation of Platelets from Gastrointestinal Cancer Patients.J Clin Med. 2019 Jun 28;8(7):936. doi: 10.3390/jcm8070936. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31261776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bence, K. K., M. Delibegovic, B. Xue, C. Z. Gorgun, G. S. Hotamisligil, B. G. Neel, and B. B. Kahn. 2006. Neuronal PTP1B regulates body weight, adiposity and leptin action. Nat. Med. 12:917-924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
