Association of saquinavir plasma concentrations with side effects but not with antiretroviral outcome in patients infected with protease inhibitor-susceptible human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- PMID: 17576836
- PMCID: PMC2043227
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00036-07
Association of saquinavir plasma concentrations with side effects but not with antiretroviral outcome in patients infected with protease inhibitor-susceptible human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Abstract
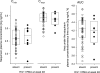
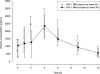
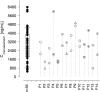
The objective of this study was to identify parameters among saquinavir pharmacokinetics, patients' demographics or comedications, to be addressed for improved personalized therapy. The presence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA at therapy week 48 (principal target parameter), CD4 cell count at week 48, infections and side effects during 48 weeks, indicators of liver toxicity and lipid abnormalities at week 48, and a 12-h saquinavir plasma concentration-versus-time profile were assessed in 56 patients receiving saquinavir-ritonavir (1,000 and 100 mg, respectively) twice daily (44 therapy-naïve and 12 antiretrovirally pretreated patients) for association with saquinavir plasma concentrations, demographics, baseline values of target parameters, and coadministered antiretrovirals. Antiretroviral failure was observed in 8 of the 56 patients in whom HIV-1 RNA was detectable at week 48. This therapeutic failure was not associated with individual saquinavir pharmacokinetics. More likely, therapeutic failure was related to incidences interfering with antiretroviral therapy, causing therapy interruptions or incompliance. Weak associations were, however, seen between high maximum saquinavir plasma concentrations and both CD4 counts of > or =200 cells microl(-1) at week 48 (P = 0.014) and constitutional side effects during 48 weeks (P = 0.002). However, patients with high CD4 counts and constitutional side effects were not identical (P = 0.53). Saquinavir therapeutic drug monitoring in patients infected with protease inhibitor-susceptible HIV-1 taking saquinavir-ritonavir (1,000 and 100 mg, respectively) is not demanded for improving the antiretroviral effect. It may be contemplated in cases with constitutional side effects or low CD4 counts with weak immune responses.
Figures

References
-
- Antoniou, T., A. L. Tseng, R. P. van Heeswijk, S. E. Walker, P. Giguere, and E. J. Phillips. 2005. Steady-state pharmacokinetics and tolerability of indinavir-lopinavir/r combination therapy in antiretroviral-experienced patients. Ther. Drug Monit. 27:779-781. - PubMed
-
- Cameron, D. W., A. J. Japour, Y. Xu, A. Hsu, J. Mellors, C. Farthing, C. Cohen, D. Poretz, M. Markowitz, S. Follansbee, J. B. Angel, D. McMahon, D. Ho, V. Devanarayan, R. Rode, M. Salgo, D. J. Kempf, R. Granneman, J. M. Leonard, and E. Sun. 1999. Ritonavir and saquinavir combination therapy for the treatment of HIV infection. AIDS 13:213-224. - PubMed
-
- Casado, J. L., S. Moreno, K. Hertogs, F. Dronda, A. Antela, P. Dehertogh, M. J. Perez-Elias, and A. Moreno. 2002. Plasma drug levels, genotypic resistance, and virological response to a nelfinavir plus saquinavir-containing regimen. AIDS 16:47-52. - PubMed
-
- Dragsted, U. B., J. Gerstoft, C. Pedersen, B. Peters, A. Duran, N. Obel, A. Castagna, P. Cahn, N. Clumeck, J. N. Bruun, J. Benetucci, A. Hill, I. Cassetti, P. Vernazza, M. Youle, Z. Fox, and J. D. Lundgren. 2003. Randomized trial to evaluate indinavir/ritonavir versus saquinavir/ritonavir in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected patients: the MaxCmin1 Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 188:635-642. - PubMed
-
- Gatti, G., A. Di Biagio, R. Casazza, C. De Pascalis, M. Bassetti, M. Cruciani, S. Vella, and D. Bassetti. 1999. The relationship between ritonavir plasma levels and side-effects: implications for therapeutic drug monitoring. AIDS 13:2083-2089. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

