Cation induced differential effect on structural and functional properties of Mycobacterium tuberculosis alpha-isopropylmalate synthase
- PMID: 17577419
- PMCID: PMC1919377
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-7-39
Cation induced differential effect on structural and functional properties of Mycobacterium tuberculosis alpha-isopropylmalate synthase
Abstract
Background: Alpha-isopropylmalate synthase (MtalphaIPMS), an enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step of the leucine biosynthetic pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a potential drug target for the anti-tuberculosis drugs. Cations induce differential effect of activation and inhibition of MtalphaIPMS. To date no concrete mechanism for such an opposite effect of similarly charged cations on the functional activity of enzyme has been presented.
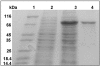
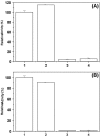
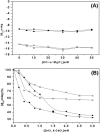
Results: Effect of cations on the structure and function of the MtalphaIPMS has been studied in detail. The studies for the first time demonstrate that different cations interact specifically at different sites in the enzyme and modulate the enzyme structure differentially. The inhibitors Zn2+ and Cd2+ ions interact directly with the catalytic domain of the enzyme and induce unfolding/denaturation of the domain. The activator K+ also interacts with the catalytic TIM barrel domain however, it does not induce any significant effect on the enzyme structure. Studies with isolated catalytic TIM barrel domain showed that it can carry out the catalytic function on its own but probably requires the non-catalytic C-terminal domain for optimum functioning. An important observation was that divalent cations induce significant interaction between the regulatory and the catalytic domain of MtalphaIPMS thus inducing structural cooperativity in the enzyme. This divalent cation induced structural cooperativity might result in modulation of activity of the catalytic domain by regulatory domain.
Conclusion: The studies for the first time demonstrate that different cations bind at different sites in the enzyme leading to their differential effects on the structure and functional activity of the enzyme.
Figures





References
-
- Kohlhaw G, Leary TR, Umbarger HE. Alpha-isopropylmalate synthase from Salmonella typhimurium. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1969;244:2218–2225. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

