Localization and characterization of the mannose-binding lectin (MBL)-associated-serine protease-2 binding site in rat ficolin-A: equivalent binding sites within the collagenous domains of MBLs and ficolins
- PMID: 17579066
- PMCID: PMC2592534
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.1.455
Localization and characterization of the mannose-binding lectin (MBL)-associated-serine protease-2 binding site in rat ficolin-A: equivalent binding sites within the collagenous domains of MBLs and ficolins
Abstract
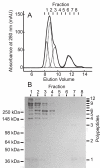
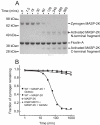
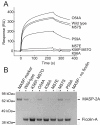
Ficolins and mannose-binding lectins (MBLs) are the first components of the lectin branch of the complement system. They comprise N-terminal collagen-like domains and C-terminal pathogen-recognition domains (fibrinogen-like domains in ficolins and C-type carbohydrate-recognition domains in MBLs), which target surface-exposed N-acetyl groups or mannose-like sugars on microbial cell walls. Binding leads to activation of MBL-associated serine protease-2 (MASP-2) to initiate complement activation and pathogen neutralization. Recent studies have shown that MASP-2 binds to a short segment of the collagen-like domain of MBL. However, the interaction between ficolins and MASP-2 is relatively poorly understood. In this study, we show that the MASP-2 binding site on rat ficolin-A is also located within the collagen-like domain and encompasses a conserved motif that is present in both MBLs and ficolins. Characterization of this motif using site-directed mutagenesis reveals that a lysine residue in the X position of the Gly-X-Y collagen repeat, Lys(56) in ficolin-A, which is present in all ficolins and MBLs known to activate complement, is essential for MASP-2 binding. Adjacent residues also make important contributions to binding as well as to MASP activation probably by stabilizing the local collagen helix. Equivalent binding sites and comparable activation kinetics of MASP-2 suggest that complement activation by ficolins and MBLs proceeds by analogous mechanisms.
Figures





References
-
- Turner MW. Mannose-binding lectin: the pluripotent molecule of the innate immune system. Immunology Today. 1996;17:532–540. - PubMed
-
- Carroll MC. The complement system in regulation of adaptive immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:981–986. - PubMed
-
- Garred P, Madsen HO, Balslev U, Hofmann B, Pedersen C, Gerstoft J, Svejgaard A. Susceptibility to HIV infection and progression of AIDS in relation to varient alleles of mannose-binding lectin. Lancet. 1997;349:236–240. - PubMed
-
- Neth O, Hann I, Turner MW, Klein NJ. Deficiency of mannose-binding lectin and burden of infection in children with malignancy: a prospective study. The Lancet. 2001;358:614–618. - PubMed
-
- Kilpatrick DC. Mannan-binding lectin: clinical significance and applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2002;1572:401–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

