TRP channels
- PMID: 17579562
- PMCID: PMC4196875
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142819
TRP channels
Abstract
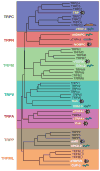
The TRP (Transient Receptor Potential) superfamily of cation channels is remarkable in that it displays greater diversity in activation mechanisms and selectivities than any other group of ion channels. The domain organizations of some TRP proteins are also unusual, as they consist of linked channel and enzyme domains. A unifying theme in this group is that TRP proteins play critical roles in sensory physiology, which include contributions to vision, taste, olfaction, hearing, touch, and thermo- and osmosensation. In addition, TRP channels enable individual cells to sense changes in their local environment. Many TRP channels are activated by a variety of different stimuli and function as signal integrators. The TRP superfamily is divided into seven subfamilies: the five group 1 TRPs (TRPC, TRPV, TRPM, TRPN, and TRPA) and two group 2 subfamilies (TRPP and TRPML). TRP channels are important for human health as mutations in at least four TRP channels underlie disease.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

