The isolation of nucleic acids from fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues-which methods are useful when?
- PMID: 17579711
- PMCID: PMC1888728
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000537
The isolation of nucleic acids from fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues-which methods are useful when?
Abstract
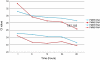
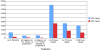
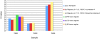
Museums and pathology collections around the world represent an archive of genetic material to study populations and diseases. For preservation purposes, a large portion of these collections has been fixed in formalin-containing solutions, a treatment that results in cross-linking of biomolecules. Cross-linking not only complicates isolation of nucleic acid but also introduces polymerase "blocks" during PCR. A wide variety of methods exists for the recovery of DNA and RNA from archival tissues, and although a number of previous studies have qualitatively compared the relative merits of the different techniques, very few have undertaken wide scale quantitative comparisons. To help address this issue, we have undertaken a study that investigates the quality of nucleic acids recovered from a test panel of fixed specimens that have been manipulated following a number of the published protocols. These include methods of pre-treating the samples prior to extraction, extraction and nucleic acid purification methods themselves, and a post-extraction enzymatic repair technique. We find that although many of the published methods have distinct positive effects on some characteristics of the nucleic acids, the benefits often come at a cost. In addition, a number of the previously published techniques appear to have no effect at all. Our findings recommend that the extraction methodology adopted should be chosen carefully. Here we provide a quick reference table that can be used to determine appropriate protocols for particular aims.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brutlag D, Schlehuber C, Bonner J. Properties of formaldehyde treated nucleohistone. Biochemistry. 1969;8:3214–3218. - PubMed
-
- Ilyin YV, Georgiev GP. Heterogeneity of deoxynucleoprotein particles as evidencec by ultracentrifugation of cesium chloride density gradient. J Mol Biol. 1969;41:299–303. - PubMed
-
- Feldman MY. Reactions of nucleic acids and nucleoproteins with formaldehyde. Prog Nucleic Acids Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:1–49. - PubMed
-
- Varshavsky A, Ilyin YV. Salt treatment of chromatin induces redistribution of histones. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1974;340:207–217.
-
- Varshavsky A, Sundin O, Bohn M. A stretch of “late” SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979;16:453–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

