Cytoplasmic volume condensation is an integral part of mitosis
- PMID: 17581282
- PMCID: PMC2042484
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.6.13.4357
Cytoplasmic volume condensation is an integral part of mitosis
Abstract
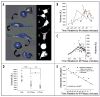
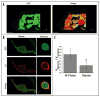
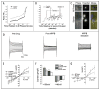
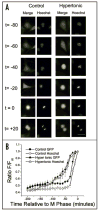
Cell growth and osmotic volume regulation are undoubtedly linked to the progression of the cell cycle as with each division, a newly generated cell must compensate for loss of half of its volume to its sister cell. The extent to which size influences cell cycle decisions, however, is controversial in mammalian cells. Further, a mechanism by which cells can monitor and therefore regulate their size has not been fully elucidated. Despite an ongoing debate, there have been few studies which directly address the question in single cell real-time experiments. In this study we used fluorescent time-lapse imaging to quantitatively assess volume in individual spontaneously dividing cells throughout the cell cycle. Together with biophysical studies, these establish that the efflux of salt and water brings about a condensation of cytoplasmic volume as glioma cells progress through mitosis. As cells undergo this pre-mitotic condensation (PMC) they approach a preferred cell volume preceding each division. This is functionally linked to chromatin condensation, suggesting that PMC plays an integral role in mitosis.
Figures

References
-
- Sveiczer A, Novak B, Mitchison JM. The size control of fission yeast revisited. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:2947–57. - PubMed
-
- Fantes PA, Nurse P. Control of the timing of cell division in fission yeast: Cell size mutants reveal a second control pathway. Exp Cell Res. 1978;115:317–29. - PubMed
-
- Rupes I. Checking cell size in yeast. Trends Genet. 2002;18:479–85. - PubMed
-
- Kellogg DR. Wee1-dependent mechanisms required for coordination of cell growth and cell division. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:24–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
