Diabetic muscle infarction
- PMID: 17582055
- PMCID: PMC2658412
- DOI: 10.1136/emj.2006.040071
Diabetic muscle infarction
Abstract
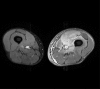
Diabetic muscle infarction (DMI) is a rare complication of longstanding, poorly controlled diabetes. Only a few cases have been reported in the literature. The case of a 34-year-old man with a 7-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, with sudden onset of left thigh pain, is described here. A final diagnosis of DMI was made, the pathophysiology of which remains unclear. MRI findings were diagnostic and characteristic. The management of this condition is usually symptomatic. Short-term prognosis is very good; however, the recurrence rate is high. Long-term prognosis is poor, with most patients dying from cardiovascular complications of diabetes within 5 years of diagnosis. This case supports the need for a high index of suspicion, when a poorly controlled patient with diabetes presents with non-traumatic limb pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Angervall L, Stener B. Tumoriform focal muscular degeneration in two diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1965139–42.
-
- Trujillo‐Santos A J. Diabetic muscle infarction: an underdiagnosed complication of long‐standing diabetes. Diabetes Care 200326211–215. - PubMed
-
- Palmer G W, Greco T P. Diabetic thigh muscle infarction in association with antiphospholipid antibodies. Semin Arthritis Rheum 200130272–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical