Differential expression of posttetanic potentiation and retrograde signaling mediate target-dependent short-term synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 17582334
- PMCID: PMC3251520
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.002
Differential expression of posttetanic potentiation and retrograde signaling mediate target-dependent short-term synaptic plasticity
Abstract
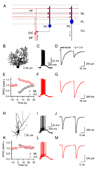
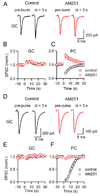
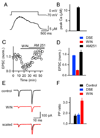
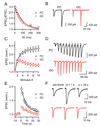
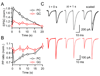
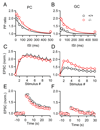
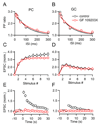
Short-term synaptic plasticity influences how presynaptic spike patterns control the firing of postsynaptic targets. Here we investigated whether specific mechanisms of short-term plasticity are regulated in a target-dependent manner by comparing synapses made by cerebellar granule cell parallel fibers onto Golgi cells (PF-->GC synapse) and Purkinje cells (PF-->PC synapse). Both synapses exhibited similar facilitation, suggesting that any differential short-term plasticity does not reflect differences in the initial release probability. PF-->PC synapses were highly sensitive to stimulus bursts, which could result in either depression of subsequent responses, mediated by endocannabinoid-dependent retrograde signaling, or enhancement of responses through posttetanic potentiation (PTP). In contrast, stimulus bursts had remarkably little effect on the strength of PF-->GC synapses. Unlike PCs, GCs were unable to regulate their PF synapses by releasing endocannabinoids. Moreover, PTP was reduced at the PF-->GC synapse compared to the PF-->PC synapse. Thus, the target-dependence of PF synapses arises from the differential expression of both retrograde signaling and PTP.
Figures

References
-
- Abbott LF, Regehr WG. Synaptic computation. Nature. 2004;431:796–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

