Modulating metastasis by a lymphangiogenic switch in prostate cancer
- PMID: 17583576
- PMCID: PMC2838420
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.22900
Modulating metastasis by a lymphangiogenic switch in prostate cancer
Abstract
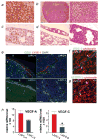
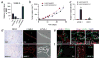
Prostate cancer dissemination is difficult to detect in the clinic, and few treatment options exist for patients with advanced-stage disease. Our aim was to investigate the role of tumor lymphangiogenesis during metastasis. Further, we implemented a noninvasive molecular imaging technique to facilitate the assessment of the metastatic process. The metastatic potentials of several human prostate cancer xenograft models, LAPC-4, LAPC-9, PC3 and CWR22Rv-1 were compared. The cells were labeled with luciferase, a bioluminescence imaging reporter gene, to enable optical imaging. After tumor implantation the animals were examined weekly during several months for the appearance of metastases. Metastatic lesions were confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Additionally, the angiogenic and lymphangiogenic profiles of the tumors were characterized. To confirm the role of lymphangiogenesis in mediating metastasis, the low-metastatic LAPC-9 tumor cells were engineered to overexpress VEGF-C, and the development of metastases was evaluated. Our results show CWR22Rv-1 and PC3 tumor cell lines to be more metastatic than LAPC-4, which in turn disseminates more readily than LAPC-9. The difference in metastatic potential correlated with the endogenous production levels of lymphangiogenic growth factor VEGF-C and the presence of tumor lymphatics. In agreement, induced overexpression of VEGF-C in LAPC-9 enhanced tumor lymphangiogenesis leading to the development of metastatic lesions. Taken together, our studies, based on a molecular imaging approach for semiquantitative detection of micrometastases, point to an important role of tumor lymphatics in the metastatic process of human prostate cancer. In particular, VEGF-C seems to play a key role in prostate cancer metastasis.
(c) 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Rockville, MD: NCI; 2006.
-
- D'Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, Fondurulia J, Chen MH, Kaplan I, Beard CJ, Tomaszewski JE, Renshaw AA, Wein A, Coleman CN. Pretreatment nomogram for prostate-specific antigen recurrence after radical prostatectomy or external-beam radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:168–72. - PubMed
-
- Stone NN, Stock RG. Laparoscopic pelvic lymph node dissection in the staging of prostate cancer. Mt Sinai J Med. 1999;66:26–30. - PubMed
-
- Shah RB, Mehra R, Chinnaiyan AM, Shen R, Ghosh D, Zhou M, Macvicar GR, Varambally S, Harwood J, Bismar TA, Kim R, Rubin MA, et al. Androgen-independent prostate cancer is a heterogeneous group of diseases: lessons from a rapid autopsy program. Cancer Res. 2004;64:9209–16. - PubMed
-
- Pound CR, Partin AW, Eisenberger MA, Chan DW, Pearson JD, Walsh PC. Natural history of progression after PSA elevation following radical prostatectomy. JAMA. 1999;281:1591–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

