Elevated expression of VEGFR-3 in lymphatic endothelial cells from lymphangiomas
- PMID: 17584927
- PMCID: PMC1925108
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-105
Elevated expression of VEGFR-3 in lymphatic endothelial cells from lymphangiomas
Abstract
Background: Lymphangiomas are neoplasias of childhood. Their etiology is unknown and a causal therapy does not exist. The recent discovery of highly specific markers for lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) has permitted their isolation and characterization, but expression levels and stability of molecular markers on LECs from healthy and lymphangioma tissues have not been studied yet. We addressed this problem by profiling LECs from normal dermis and two children suffering from lymphangioma, and also compared them with blood endothelial cells (BECs) from umbilical vein, aorta and myometrial microvessels.
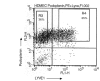
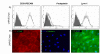
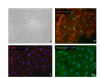
Methods: Lymphangioma tissue samples were obtained from two young patients suffering from lymphangioma in the axillary and upper arm region. Initially isolated with anti-CD31 (PECAM-1) antibodies, the cells were separated by FACS sorting and magnetic beads using anti-podoplanin and/or LYVE-1 antibodies. Characterization was performed by FACS analysis, immunofluorescence staining, ELISA and micro-array gene analysis.
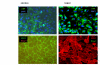
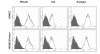
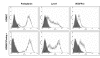
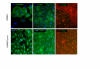
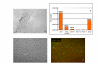
Results: LECs from foreskin and lymphangioma had an almost identical pattern of lymphendothelial markers such as podoplanin, Prox1, reelin, cMaf and integrin-alpha1 and -alpha9. However, LYVE-1 was down-regulated and VEGFR-2 and R-3 were up-regulated in lymphangiomas. Prox1 was constantly expressed in LECs but not in any of the BECs.
Conclusion: LECs from different sources express slightly variable molecular markers, but can always be distinguished from BECs by their Prox1 expression. High levels of VEGFR-3 and -2 seem to contribute to the etiology of lymphangiomas.
Figures



References
-
- Wilting J. Integrated anatomy of the vascular system. In: Lanzer P, Topol E, editor. Panvascular Medicine. Heidelberg, New York: Springer; 2002. pp. 50–75.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

