miR-200b mediates post-transcriptional repression of ZFHX1B
- PMID: 17585049
- PMCID: PMC1924904
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.586807
miR-200b mediates post-transcriptional repression of ZFHX1B
Abstract
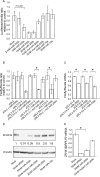
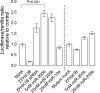
MicroRNAs have important functions during animal development and homeostasis through post-transcriptional regulation of their cognate mRNA targets. ZFHX1B is a transcriptional repressor involved in the TGFbeta signaling pathway and in processes of epithelial to mesenchymal transition via regulation of E-cadherin. We show that Zfhx1b and miR-200b are regionally coexpressed in the adult mouse brain and that miR-200b represses the expression of Zfhx1b via multiple sequence elements present in the 3'-untranslated region. Overexpression of miR-200b leads to repression of endogenous ZFHX1B, and inhibition of miR-200b relieves the repression of ZFHX1B. In accordance with these findings, miR-200b regulates the activity of the E-cadherin promoter.
Figures


References
-
- Allen Brain Atlas. Seattle, WA: Allen Institute for Brain Science. 2004. http://www.brain-map.org.
-
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bagga, S., Bracht, J., Hunter, S., Massirer, K., Holtz, J., Eachus, R., Pasquinelli, A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bassez, G., Camand, O.J., Cacheux, V., Kobetz, A., Dastot-Le Moal, F., Marchant, D., Catala, M., Abitbol, M., Goossens, M. Pleiotropic and diverse expression of ZFHX1B gene transcripts during mouse and human development supports the various clinical manifestations of the “Mowat–Wilson” syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004;15:240–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
