Rigidification of neutral lipid bilayers in the presence of salts
- PMID: 17586572
- PMCID: PMC1989724
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.107.112615
Rigidification of neutral lipid bilayers in the presence of salts
Abstract
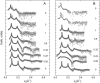
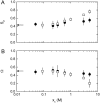
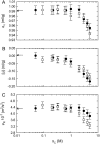
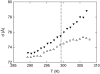
We studied the influence of sodium and calcium chloride on the global and local membrane properties of fluid palmitoyl-oleoyl phosphatidylcholine bilayers, applying synchrotron small-angle x-ray diffraction, spin-labeling electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry, as well as simultaneous density and acoustic measurements. The salt concentration was varied over a wide range from 0 to 5 M. We found that NaCl leads to a continuous swelling of the bilayers, whereas the behavior of the bilayer separation dW in the presence of CaCl2 is more complex, showing an initial large dW value, which decreased upon further addition of salt and finally increased again in the high concentration regime. This can be understood by a change of balance between electrostatic and van der Waals interactions. We were further able to show that both salts lead to a significant increase of order within the lipid bilayer, leading to a decrease of bilayer elasticity and shift of main phase transition temperature. This effect is more pronounced for Ca2+, and occurs mainly in the high salt-concentration regime. Thus, we were able to reconcile previous controversies between molecular dynamics simulations and x-ray diffraction experiments regarding the effect of salts on neutral lipid bilayers.
Figures



References
-
- Inoko, Y., T. Yamaguchi, K. Furuya, and T. Mitsui. 1975. Effects of cations on dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol/water systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 413:24–32. - PubMed
-
- Lis, L. J., W. T. Lis, V. A. Parsegian, and R. P. Rand. 1981. Adsorption of divalent cations to a variety of phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 20:1771–1777. - PubMed
-
- Lis, L. J., V. A. Parsegian, and R. P. Rand. 1981. Binding of divalent cations of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers and its effect on bilayer interaction. Biochemistry. 20:1761–1770. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham, B. A., and L. J. Lis. 1986. Thiocyanate and bromide ions influence the bilayer structural parameters of phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 861:237–242. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham, B. A., J. E. Shimotake, W. Tamura-Lis, T. Mastran, W. M. Kwok, J. W. Kauffman, and L. J. Lis. 1986. The influence of ion species on phosphatidylcholine bilayer structure and packing. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 39:135–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

