Inactivation of thioredoxin reductases reveals a complex interplay between thioredoxin and glutathione pathways in Arabidopsis development
- PMID: 17586656
- PMCID: PMC1955716
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.107.050849
Inactivation of thioredoxin reductases reveals a complex interplay between thioredoxin and glutathione pathways in Arabidopsis development
Abstract
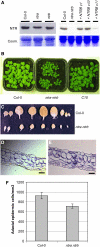
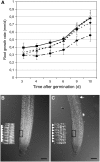
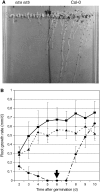
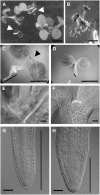
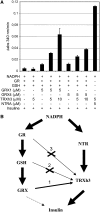
NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductases (NTRs) are key regulatory enzymes determining the redox state of the thioredoxin system. The Arabidopsis thaliana genome has two genes coding for NTRs (NTRA and NTRB), both of which encode mitochondrial and cytosolic isoforms. Surprisingly, plants of the ntra ntrb knockout mutant are viable and fertile, although with a wrinkled seed phenotype, slower plant growth, and pollen with reduced fitness. Thus, in contrast with mammals, our data demonstrate that neither cytosolic nor mitochondrial NTRs are essential in plants. Nevertheless, in the double mutant, the cytosolic thioredoxin h3 is only partially oxidized, suggesting an alternative mechanism for thioredoxin reduction. Plant growth in ntra ntrb plants is hypersensitive to buthionine sulfoximine (BSO), a specific inhibitor of glutathione biosynthesis, and thioredoxin h3 is totally oxidized under this treatment. Interestingly, this BSO-mediated growth arrest is fully reversible, suggesting that BSO induces a growth arrest signal but not a toxic accumulation of activated oxygen species. Moreover, crossing ntra ntrb with rootmeristemless1, a mutant blocked in root growth due to strongly reduced glutathione synthesis, led to complete inhibition of both shoot and root growth, indicating that either the NTR or the glutathione pathway is required for postembryonic activity in the apical meristem.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Accumulation of flavonoids in an ntra ntrb mutant leads to tolerance to UV-C.Mol Plant. 2009 Mar;2(2):249-58. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssn065. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Mol Plant. 2009. PMID: 19825611
-
Nitric oxide is required for the auxin-induced activation of NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductase and protein denitrosylation during root growth responses in arabidopsis.Ann Bot. 2015 Sep;116(4):695-702. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcv116. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Ann Bot. 2015. PMID: 26229066 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductase A (NTRA) confers elevated tolerance to oxidative stress and drought.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Jul;80:184-91. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 Apr 19. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24792388
-
Stress defense mechanisms of NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductases (NTRs) in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2015;10(5):e1017698. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2015.1017698. Plant Signal Behav. 2015. PMID: 26039478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase.Eur J Biochem. 2000 Oct;267(20):6102-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01701.x. Eur J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11012661 Review.
Cited by
-
Two distinct redox cascades cooperatively regulate chloroplast functions and sustain plant viability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 5;113(27):E3967-76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604101113. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27335455 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species and the Redox-Regulatory Network in Cold Stress Acclimation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Nov 21;7(11):169. doi: 10.3390/antiox7110169. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30469375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix Redox Physiology Governs the Regulation of Plant Mitochondrial Metabolism through Posttranslational Protein Modifications.Plant Cell. 2020 Mar;32(3):573-594. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00535. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 31911454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plastid thioredoxins: a "one-for-all" redox-signaling system in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Nov 21;4:463. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00463. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 24319449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatio-temporal relief from hypoxia and production of reactive oxygen species during bud burst in grapevine (Vitis vinifera).Ann Bot. 2015 Sep;116(4):703-11. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcv123. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Ann Bot. 2015. PMID: 26337519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408 796–815. - PubMed
-
- Arner, E.S., and Holmgren, A. (2000). Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur. J. Biochem. 267 6102–6109. - PubMed
-
- Balmer, Y., Vensel, W.H., Tanaka, C.K., Hurkman, W.J., Gelhaye, E., Rouhier, N., Jacquot, J.-P., Manieri, W., Schurmann, P., Droux, M., and Buchanan, B.B. (2004). Thioredoxin links redox to the regulation of fundamental processes of plant mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101 2642–2647. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

