Immune modulation of HLA-G dimer in maternal-fetal interface
- PMID: 17587197
- PMCID: PMC2991771
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200737515
Immune modulation of HLA-G dimer in maternal-fetal interface
Abstract
HLA-G is a non-classical human MHC class I molecule, which has several characteristics distinct from classical MHC, such as low polymorphism and restricted tissue distribution. HLA-G is expressed on placenta, thymus and some tumors. At the maternal-fetal interface, trophoblasts do not express major classical MHC class I molecules (MHCI), HLA-A and -B, to prevent normal T cell responses. Instead, HLA-G is expressed and can suppress a wide range of immune responses by binding to inhibitory immune cell surface receptors, such as leukocyte Ig-like receptor (LILR) B1 and LILRB2. HLA-G exists in various forms, including beta2m-associated or -free disulfide-linked dimers that can be expressed either at the cell surface or in soluble form. However, until recently the physiological role of these different molecular forms has been unclear. In this issue of the European Journal of Immunology, one article demonstrates that the disulfide-linked homodimer of beta2m-associated HLA-G is the major fraction expressed by trophoblast cells. The HLA-G dimer modulates the function of LILRB1-expressing antigen-presenting cells by principally binding to LILRB1. On the other hand, another recent report showed that beta2m-free disulfide-linked HLA-G dimers are produced by villous cytotrophoblast cells. Taken together, these results provide strong evidence in support of the hypothesis that HLA-G dimers play a role in immune suppression at the maternal-fetal interface. Further in-depth investigation will help to clarify the precise mechanism of HLA-G receptor recognition and signaling in vivo and the role of these interactions in successful reproduction. See accompanying article: (http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/eji.200737089).
Figures
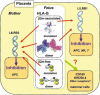
Comment on
-
A homodimeric complex of HLA-G on normal trophoblast cells modulates antigen-presenting cells via LILRB1.Eur J Immunol. 2007 Jul;37(7):1924-37. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737089. Eur J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17549736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hunt JS, Petroff MG, McIntire RH, Ober C. HLA-G and immune tolerance in pregnancy. FASEB J. 2005;19:681–693. - PubMed
-
- Colonna M, Nakajima H, Cella M. Inhibitory and activating receptors involved in immune surveillance by human NK and myeloid cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999;66:718–722. - PubMed
-
- O'Callaghan CA, Bell JI. Structure and function of the human MHC class Ib molecules HLA-E, HLA-F and HLA-G. Immunol. Rev. 1998;163:129–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

