Genetic relatedness among isolates of Shigella sonnei carrying class 2 integrons in Tehran, Iran, 2002-2003
- PMID: 17587439
- PMCID: PMC1914347
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-7-62
Genetic relatedness among isolates of Shigella sonnei carrying class 2 integrons in Tehran, Iran, 2002-2003
Abstract
Background: Shigella spp. are major cause of diarrhoeal disease in both developing and developed countries. Shigella sonnei is the serogroup of Shigella most frequently responsible for sporadic and epidemic enteritis in developed countries. In recent years the emergence and spread of S. sonnei biotype g carrying class 2 integron have been frequently reported in many countries. Recently, S. sonnei has been reported as the prevalent serogroup of Shigella in Iran. The present study was carried out to investigate phenotypic and genetic characteristics of Shigella sonnei isolates identified in the years 2002 and 2003 in Tehran, Iran.
Methods: Biotyping, drug susceptibility testing, pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and analysis of class 2 integrons have been carried out on 60 S. sonnei isolates, including 57 sporadic isolates from paediatric cases of shigellosis occurring in 2002 and 2003, two sporadic isolates recovered in 1984 and the ATCC 9290 strain.
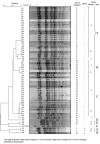
Results: Biotype g and resistance to streptomycin, sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim and tetracycline were exhibited by 54 of the 57 recent isolates. Of the 54 biotype g isolates, 28 exhibited a class 2 integron of 2161 bp, and 24 a class 2 integron of 1371 bp, respectively. Class 2 integrons were not detected in four isolates only, including the two endemic isolates recovered in 1984 and two strains from recent sporadic cases. PFGE divided the strains into eight pulsotypes labeled A to H, three major pulsotypes - A to C - including the large majority of the recent sporadic S. sonnei isolates. Pulsotypes A and C were the most prevalent groups, accounting for 41.6% and 35.0%, respectively, of the isolates under study.
Conclusion: The results suggest that biotype g, class 2 integron carrying S. sonnei are prevalent in our geographic area. S. sonnei isolated in the years 2002 and 2003 could be attributed to a few predominant clusters including, respectively, strains with pulsotypes B and C carrying a 2161 bp class 2 integron, and those having pulsotype A and a 1371 bp class 2 integron. A few epidemic clones are responsible for the apparently endemic occurrence of shigellosis in Tehran, Iran.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Shigella sonnei biotype G carrying class 2 integrons in southern Italy: a retrospective typing study by pulsed field gel electrophoresis.BMC Infect Dis. 2006 Jul 17;6:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-117. BMC Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16846516 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Shigella sonnei biotype g isolates carrying class 2 integrons in Italy (2001 to 2003).J Clin Microbiol. 2005 May;43(5):2467-70. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.5.2467-2470.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15872285 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characteristics of class 1 and class 2 integrons and their relationships to antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006 Aug;58(2):288-96. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl228. Epub 2006 Jun 9. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16766536
-
The importance of integrons for development and propagation of resistance in Shigella: the case of Latin America.Braz J Microbiol. 2016 Oct-Dec;47(4):800-806. doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2016.07.019. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Braz J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27528086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short report: analysis of clonal relationship among Shigella sonnei isolates circulating in Argentina.Epidemiol Infect. 2007 May;135(4):681-7. doi: 10.1017/S0950268806007230. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Epidemiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 16999876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The occurrence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Shigella spp. in Tehran, Iran.Iran J Microbiol. 2013 Jun;5(2):108-12. Iran J Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23825726 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical class 1 integron coexists with class 1 and class 2 integrons in multi-drug resistant Shigella flexneri isolates from China.Curr Microbiol. 2011 Mar;62(3):802-6. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9790-3. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Curr Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20976456
-
Characterization of WRSs2 and WRSs3, new second-generation virG(icsA)-based Shigella sonnei vaccine candidates with the potential for reduced reactogenicity.Vaccine. 2010 Feb 10;28(6):1642-54. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.11.001. Epub 2009 Nov 20. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 19932216 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Sensitivity Patterns and Molecular Typing of Shigella sonnei Strains Using ERIC-PCR.Iran J Public Health. 2013 Oct;42(10):1151-7. Iran J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 26060624 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial CRISPR Regions: General Features and their Potential for Epidemiological Molecular Typing Studies.Open Microbiol J. 2018 Apr 23;12:59-70. doi: 10.2174/1874285801812010059. eCollection 2018. Open Microbiol J. 2018. PMID: 29755603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bennish ML, Wojtyniak BJ. Mortality due to shigellosis: community and hospital data. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:S245–S251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous