Transcriptional response of pancreatic beta cells to metabolic stimulation: large scale identification of immediate-early and secondary response genes
- PMID: 17587450
- PMCID: PMC1914353
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-54
Transcriptional response of pancreatic beta cells to metabolic stimulation: large scale identification of immediate-early and secondary response genes
Abstract
Background: Physiological long term adaptation of pancreatic beta cells is driven by stimuli such as glucose and incretin hormones acting via cAMP (e.g. GLP-1) and involves regulated gene expression. Several rapidly inducible immediate-early genes (IEGs) have been identified in beta cells. Many of these IEGs code for transcription factors and have the potential to control the transcription of downstream target genes likely involved in long term cellular adaptation. The identity of these target genes has not been determined, and the sequence of events occurring during beta cell adaptation is still unclear.
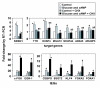
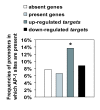
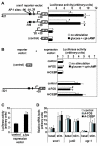
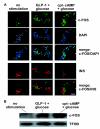
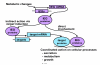
Results: We have developed a microarray-based strategy for the systematic search of targets. In Min6 insulin-secreting cells, we identified 592 targets and 1278 IEGs responding to a co-stimulation with glucose and cAMP. Both IEGs and targets were involved in a large panel of functions, including those important to beta cell physiology (metabolism, secretion). Nearly 200 IEGs were involved in signaling and transcriptional regulation. To find specific examples of the regulatory link between IEGs and targets, target promoter sequences were analyzed in silico. Statistically significant over-representation of AP-1 response elements notably suggested an important role for this transcription factor, which was experimentally verified. Indeed, cell stimulation altered expression of IEG-encoded components of the AP-1 complex, activating AP-1-dependent transcription. Loss and gain-of-function experiments furthermore allowed to validate a new AP-1 regulated gene (sulfiredoxin) among the targets. AP-1 and sulfiredoxin are sequentially induced also in primary cells from rat islets of Langerhans.
Conclusion: By identifying IEGs and their downstream targets, this study brings a comprehensive description of the transcriptional response occurring after beta cell stimulation, as well as new mechanistic insights concerning the AP-1 transcription factor.
Figures




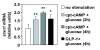
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation underlying temporal integration of signals.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(18):5175-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl654. Epub 2006 Sep 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16998184 Free PMC article.
-
In silico identification of NF-kappaB-regulated genes in pancreatic beta-cells.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Feb 15;8:55. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-55. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17302974 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of PTB1 promotes the expression of insulin secretory granule proteins in beta cells.Cell Metab. 2006 Feb;3(2):123-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.12.008. Cell Metab. 2006. PMID: 16459313
-
Modulation of cyclic nucleotides and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases in pancreatic islet beta-cells and intestinal L-cells as targets for treating diabetes mellitus.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 Oct;7(10):898-905. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006. PMID: 17086934 Review.
-
New insights into the role of cAMP in the production and function of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1).Cell Signal. 2010 Jan;22(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.032. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 19772917 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of primary response genes.Mol Cell. 2011 Nov 4;44(3):348-60. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.09.014. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22055182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sitagliptin reduces cardiac apoptosis, hypertrophy and fibrosis primarily by insulin-dependent mechanisms in experimental type-II diabetes. Potential roles of GLP-1 isoforms.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 21;8(10):e78330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078330. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24302978 Free PMC article.
-
SRXN1 is a novel protective factor against methylmercury-induced apoptosis in C17.2 mouse neural stem cells.Toxicol Res. 2025 Jan 3;41(2):167-173. doi: 10.1007/s43188-024-00277-6. eCollection 2025 Mar. Toxicol Res. 2025. PMID: 40013080
-
Effect of dietary restriction and subsequent re-alimentation on the transcriptional profile of bovine jejunal epithelium.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 19;13(3):e0194445. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194445. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29554113 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomic profiling of human pancreatic islets reveals genes responsive to glucose exposure over 24 h.Diabetologia. 2024 Oct;67(10):2246-2259. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06214-4. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38967666 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

