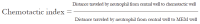Effects of four Indian medicinal herbs on Isoniazid-, Rifampicin- and Pyrazinamide-induced hepatic injury and immunosuppression in guinea pigs
- PMID: 17589898
- PMCID: PMC4436605
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3199
Effects of four Indian medicinal herbs on Isoniazid-, Rifampicin- and Pyrazinamide-induced hepatic injury and immunosuppression in guinea pigs
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate and compare the hepatoprotective and immunomodulatory effects of Curcuma longa (CL), Ocimum sanctum (OS), Tinospora cordifolia (TC) and Zizyphus mauritiana (ZM) on liver injury and immunosuppression induced by Isoniazid (INH), Rifampicin (RIF) and Pyrazinamide (PZA).
Methods: Duncan Hartley guinea pigs, weighing 700-1050 g, were treated orally with 50 mg/kg of INH, 100 mg/kg of RIF and 300 mg/kg of PZA for 21-d. 200 mg/kg (bw) of each herb crude extract was administered to the herb control group and 2-h previous to INH+RIF+PZA (AKT) doses to the Herb+AKT groups. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspertate aminotransferase (AST) bilirubin and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) were assessed on d 0 and 21 in all the groups. Phagocytic % (P%), Phagocytic Index (PI) and Chemotactic Index (CI) were also measured as immunologic parameters. Histological analysis was carried out to assess injury to the liver.
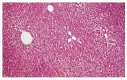
Results: The AKT treated control group showed hepatotoxicity as judged by elevated serum AST 5-fold, AST/ALT ratio 4-fold, ALP 2-fold and hepatological changes, such as focal necrosis, portal triaditis and steatosis. Immune function was suppressed as judged by decreased P% (51.67+/-1.68 vs 40.61+/-1.28, P<0.01), PI (2.0725+/-0.05 vs 0.61+/-0.05, P<0.001) and CI (1.8525+/-0.04 vs 0.695+/-0.07, P<0.001). All four herb treated groups showed normal liver histology, enzyme levels and increased P%, while PI and CI were enhanced in the TC and ZM treated groups, respectively. CL+AKT, TC+AKT and ZM+AKT showed nearly normal histology with minimal inflammation and microvesicular steatosis, while OS+AKT showed partial protection. Hepatotoxicity was prevented by restricting the rise of AST by 2-fold in CL+AKT and TC+AKT groups and by 3-fold in OS+AKT and ZM+AKT groups, AST/ALT by 2-fold and ALP to normal levels in all four groups. All four herb+AKT groups showed normal to enhanced neutrophil function.
Conclusion: All four herbs showed hepatoprotective potential and prevented immunosuppression. CL and TC showed the highest hepatoprotective activity, while TC and ZM showed strong immunostimulatory activity.
Figures
References
-
- Raviglione MC, Snider DE, Kochi A. Global epidemiology of tuberculosis. Morbidity and mortality of a worldwide epidemic. JAMA. 1995;273:220–226. - PubMed
-
- WHO Report. Global tuberculosis control, surveillance, planning, financing. Geneva: World Health Organization. WHO document WHO/CDS/TB/; 2002. p. 295.
-
- Mahashur AA, Prabhudesai PP. Hepatitis and antitubercular therapy. J Assoc Physicians India. 1991;39:595–596. - PubMed
-
- Steele MA, Burk RF, DesPrez RM. Toxic hepatitis with isoniazid and rifampin. A meta-analysis. Chest. 1991;99:465–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous