Inverted cystic tubulovillous adenoma involving Brunner's glands of duodenum
- PMID: 17589910
- PMCID: PMC4436617
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3262
Inverted cystic tubulovillous adenoma involving Brunner's glands of duodenum
Abstract
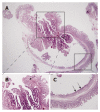
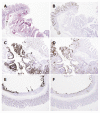
Benign neoplasia of the duodenum are very rare. Moreover, duodenal tubulovillous adenomas are more uncommon lesions. The microscopic structure of tubulovillous adenoma has frond-like projection of mucosa with branching papillary structure and generally upward growth into the lumen. We describe a 72-year-old man who showed aduodenal tubulovillous adenoma with unusual inverted cystic growth pattern. Interestingly, this tubulovillous adenomatous lesion was interrupted by gastric metaplasia in the deep portion of the cyst and was closely surrounded by Brunner's glands. Although histogenesis of gastric metaplasia of duodenum is not fully understood, Brunner's glands has been suggested as a precursor for gastric metaplasia. Therefore, these findings argued that this adenoma arises from Brunner's glands through gastric metaplasia. This is the first case of inverted cystic tubulovillous adenoma involving Brunner's glands of duodenum with gastric metaplasia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sporadic Non-ampullary Duodenal Adenoma Overriding the Cystic Dilatation of Brunner's Gland Hyperplasia.Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep 25;70(3):141-144. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2017.70.3.141. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28934830
-
Polypoid hamartoma of Brunner's gland of the duodenum.Dig Surg. 1999;16(5):431-3. doi: 10.1159/000018761. Dig Surg. 1999. PMID: 10567807
-
[Endoscopic resection of a giant duodenal Brunner's gland adenoma].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008 Aug;52(2):106-9. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 19077502 Korean.
-
Brunner's gland adenoma of duodenum: report of two cases.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):7565-9. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26261670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brunner's gland adenoma of duodenum: a case report and literature review.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Sep 1;10(17):2616-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2616. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15300922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopic Papillectomy for Ampullary Adenoma Adjacent to a Cystic Lesion.Cureus. 2025 Mar 27;17(3):e81318. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81318. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40291207 Free PMC article.
-
Small Intestinal Tumors: A Rare Case of Tubulovillous Adenoma in Duodenum.Cureus. 2019 May 15;11(5):e4671. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4671. Cureus. 2019. Retraction in: Cureus. 2019 Aug 6;11(8):r15. doi: 10.7759/cureus.r15. PMID: 31328063 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Adenocarcinoma In Situ Arising from Brunner's Gland Treated by Endoscopic Mucosal Resection.Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2017;2017:7916976. doi: 10.1155/2017/7916976. Epub 2017 Apr 23. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2017. PMID: 28512587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakorafas GH, Friess H, Dervenis CG. Villous tumors of the duodenum: biologic characters and clinical implications. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000;35:337–344. - PubMed
-
- Jepsen JM, Persson M, Jakobsen NO, Christiansen T, Skoubo-Kristensen E, Funch-Jensen P, Kruse A, Thommesen P. Prospective study of prevalence and endoscopic and histopathologic characteristics of duodenal polyps in patients submitted to upper endoscopy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994;29:483–487. - PubMed
-
- Komorowski RA, Cohen EB. Villous tumors of the duodenum: a clinicopathologic study. Cancer. 1981;47:1377–1386. - PubMed
-
- Hanby AM, Poulsom R, Elia G, Singh S, Longcroft JM, Wright NA. The expression of the trefoil peptides pS2 and human spasmolytic polypeptide (hSP) in 'gastric metaplasia' of the proximal duodenum: implications for the nature of 'gastric metaplasia'. J Pathol. 1993;169:355–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

