IL-10 measurement in aqueous humor for screening patients with suspicion of primary intraocular lymphoma
- PMID: 17591896
- PMCID: PMC2078609
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.06-0031
IL-10 measurement in aqueous humor for screening patients with suspicion of primary intraocular lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the value of IL-10 measurement in aqueous humor (AH) for screening in primary intraocular lymphoma (PIOL).
Methods: One hundred consecutive diagnostic or therapeutic vitrectomies were performed in patients with uveitis. During surgery, 100 microL of both AH and pure vitreous was taken. IL-10 levels were determined with a standard quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique. Patients were distributed in two groups: 51 patients with proven PIOL, 108 patients with uveitis divided into 74 with uveitis of proven etiology and 34 with idiopathic uveitis. Groups were compared by ANOVA and the Tukey-Kramer test or nonparametric Wilcoxon test. Distributions were compared by using the chi(2) test. Segmentation was derived from the ROC curves by choosing a tradeoff between sensitivity and specificity.
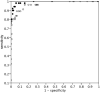
Results: In patients with PIOL, IL-10 mean values were 2205.5 pg/mL (median: 1467 pg/mL) in the vitreous and 543.4 pg/mL (median: 424 pg/mL) in AH. In patients with uveitis (idiopathic and diagnostic uveitis), mean values were 26.6 pg/mL (median: 8 pg/mL) in the vitreous, and 21.9 pg/mL (median: 8 pg/mL) in AH. IL-10 mean values were significantly different between patients with PIOL and patients with uveitis (P < 10(-3)). The areas under the curves were 0.989 and 0.962 for vitreous and AH, respectively. A cutoff of 50 pg/mL in the AH was associated with a sensitivity of 0.89 and a specificity of 0.93. In the vitreous, a cutoff value of 400 pg/mL yielded a specificity of 0.99 and a sensitivity of 0.8.
Conclusions: Diagnosis of PIOL is often made months or years after the initial onset of ocular symptoms. Cytology remains the gold standard for diagnosis. However, measurement of IL-10 in the AH is a good screening test to reduce diagnostic delays.
Figures



References
-
- Levy-Clarke GA, Buggage RR, Shen D, Vaughn LO, Chan CC, Davis JL. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 associated t-cell leukemia/lymphoma masquerading as necrotizing retinal vasculitis. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:1717–1722. - PubMed
-
- Davis J. Diagnosis of intraocular lymphoma. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2004;12:7–16. - PubMed
-
- Hochberg FH, Miller D. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Neurosurg. 1988;68:835–853. - PubMed
-
- Cassoux N, Merle-Beral H, Leblond V, et al. Ocular and central nervous system lymphoma: clinical features and diagnosis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2000;8:243–250. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

