Potent activity of carfilzomib, a novel, irreversible inhibitor of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, against preclinical models of multiple myeloma
- PMID: 17591945
- PMCID: PMC2200918
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-065888
Potent activity of carfilzomib, a novel, irreversible inhibitor of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, against preclinical models of multiple myeloma
Abstract
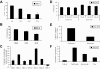
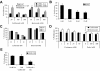
The proteasome has emerged as an important target for cancer therapy with the approval of bortezomib, a first-in-class, reversible proteasome inhibitor, for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM). However, many patients have disease that does not respond to bortezomib, whereas others develop resistance, suggesting the need for other inhibitors with enhanced activity. We therefore evaluated a novel, irreversible, epoxomicin-related proteasome inhibitor, carfilzomib. In models of MM, this agent potently bound and specifically inhibited the chymotrypsin-like proteasome and immunoproteasome activities, resulting in accumulation of ubiquitinated substrates. Carfilzomib induced a dose- and time-dependent inhibition of proliferation, ultimately leading to apoptosis. Programmed cell death was associated with activation of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, release of cytochrome c, and activation of both intrinsic and extrinsic caspase pathways. This agent also inhibited proliferation and activated apoptosis in patient-derived MM cells and neoplastic cells from patients with other hematologic malignancies. Importantly, carfilzomib showed increased efficacy compared with bortezomib and was active against bortezomib-resistant MM cell lines and samples from patients with clinical bortezomib resistance. Carfilzomib also overcame resistance to other conventional agents and acted synergistically with dexamethasone to enhance cell death. Taken together, these data provide a rationale for the clinical evaluation of carfilzomib in MM.
Figures
References
-
- Ciechanover A. Proteolysis: from the lysosome to ubiquitin and the proteasome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Orlowski M, Wilk S. Catalytic activities of the 20 S proteasome, a multicatalytic proteinase complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000;383:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Rock KL, Gramm C, Rothstein L, et al. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell. 1994;78:761–771. - PubMed
-
- Rock KL, York IA, Saric T, Goldberg AL. Protein degradation and the generation of MHC class I-presented peptides. Adv Immunol. 2002;80:1–70. - PubMed
-
- Rivett AJ, Hearn AR. Proteasome function in antigen presentation: immunoproteasome complexes, peptide production, and interactions with viral proteins. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2004;5:153–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

