PSNCBAM-1, a novel allosteric antagonist at cannabinoid CB1 receptors with hypophagic effects in rats
- PMID: 17592509
- PMCID: PMC2190018
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707347
PSNCBAM-1, a novel allosteric antagonist at cannabinoid CB1 receptors with hypophagic effects in rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Rimonabant (Acomplia, SR141716A), a cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist, has recently been approved for the treatment of obesity. There are, however, concerns regarding its side effect profile. Developing a CB1 antagonist with a different pharmacological mechanism may lead to a safer alternative. To this end we have screened a proprietary small molecule library and have discovered a novel class of allosteric antagonist at CB1 receptors. Herein, we have characterized an optimized prototypical molecule, PSNCBAM-1, and its hypophagic effects in vivo.
Experimental approach: A CB1 yeast reporter assay was used as a primary screen. PSNCBAM-1 was additionally characterized in [35S]-GTPgammaS, cAMP and radioligand binding assays. An acute rat feeding model was used to evaluate its effects on food intake and body weight in vivo.
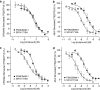
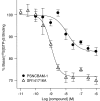
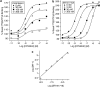
Key results: In CB1 receptor yeast reporter assays, PSNCBAM-1 blocked the effects induced by agonists such as CP55,940, WIN55212-2, anandamide (AEA) or 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG). The antagonist characteristics of PSNCBAM-1 were confirmed in [35S]-GTPgammaS binding and cAMP assays and was shown to be non-competitive by Schild analyses. PSNCBAM-1 did not affect CB2 receptors. In radioligand binding assays, PSNCBAM-1 increased the binding of [3H]CP55,940 despite its antagonist effects. In an acute rat feeding model, PSNCBAM-1 decreased food intake and body weight.
Conclusions and implications: PSNCBAM-1 exerted its effects through selective allosteric modulation of the CB1 receptor. The acute effects on food intake and body weight induced in rats provide a first report of in vivo activity for an allosteric CB1 receptor antagonist.
Figures
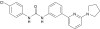
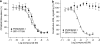
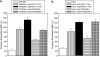
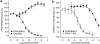

Comment in
-
Tuning the endocannabinoid system: allosteric modulators of the CB1 receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(5):565-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707349. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17592508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bensaid M, Gary-Bobo M, Esclangon A, Maffrand JP, Le Fur G, Oury-Donat F, et al. The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716 increases Acrp30 mRNA expression in adipose tissue of obese fa/fa rats and in cultured adipocyte cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63:908–914. - PubMed
-
- Birdsall NJ, Lazareno S, Matsui H. Allosteric regulation of muscarinic receptors. Prog Brain Res. 1996;109:147–151. - PubMed
-
- Bloxham J, Fyfe MCT, Horswill J, Jeevaratnam RP, Keily J, Procter MJ, et al. Arylurea derivatives International Patent Application Publication 2006. WO 2006/018662
-
- Bouaboula M, Perrachon S, Milligan l, Canat X, Rinaldi-Carmona M, Portier M, et al. A selective inverse agonist for central cannabinoid receptor inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase activation stimulated by insulin or insulin-like growth factor 1. Evidence for a new model of receptor/ligand interaction. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22330–22339. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

