Understanding the natural biology of kidney cancer: implications for targeted cancer therapy
- PMID: 17592537
- PMCID: PMC1892626
Understanding the natural biology of kidney cancer: implications for targeted cancer therapy
Abstract
During the past several decades, there has been a significant increase in the understanding of the biology, clinical behavior, and prognostic factors of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Such progress has led to greater sophistication in the diagnosis and classification of RCC. Here, we review recent advances in our knowledge of the biologic characteristics of RCC that have resulted in notable achievements in staging, prognosis, patient selection, and treatment.
Figures
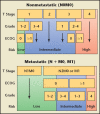
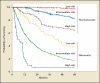
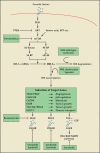
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:106–130. - PubMed
-
- Pantuck AJ, Zisman A, Belldegrun AS. The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2001;166:1611–1623. - PubMed
-
- Patard JJ, Rodriguez A, Rioux-Leclercq N, et al. Prognostic significance of the mode of detection in renal tumours. BJU Int. 2002;90:358–363. - PubMed
-
- Tsui KH, Shvarts O, Smith RB, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: prognostic significance of incidentally detected tumors. J Urol. 2000;163:426–430. - PubMed
-
- Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Wieder J, et al. Risk group assessment and clinical outcome algorithm to predict the natural history of patients with surgically resected renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4559–4566. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
