Interaction of salivary alpha-amylase and amylase-binding-protein A (AbpA) of Streptococcus gordonii with glucosyltransferase of S. gordonii and Streptococcus mutans
- PMID: 17593303
- PMCID: PMC3225810
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-60
Interaction of salivary alpha-amylase and amylase-binding-protein A (AbpA) of Streptococcus gordonii with glucosyltransferase of S. gordonii and Streptococcus mutans
Abstract
Background: Glucosyltransferases (Gtfs), enzymes that produce extracellular glucans from dietary sucrose, contribute to dental plaque formation by Streptococcus gordonii and Streptococcus mutans. The alpha-amylase-binding protein A (AbpA) of S. gordonii, an early colonizing bacterium in dental plaque, interacts with salivary amylase and may influence dental plaque formation by this organism. We examined the interaction of amylase and recombinant AbpA (rAbpA), together with Gtfs of S. gordonii and S. mutans.
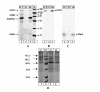
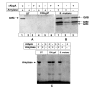
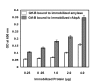
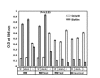
Results: The addition of salivary alpha-amylase to culture supernatants of S. gordonii precipitated a protein complex containing amylase, AbpA, amylase-binding protein B (AbpB), and the glucosyltransferase produced by S. gordonii (Gtf-G). rAbpA was expressed from an inducible plasmid, purified from Escherichia coli and characterized. Purified rAbpA, along with purified amylase, interacted with and precipitated Gtfs from culture supernatants of both S. gordonii and S. mutans. The presence of amylase and/or rAbpA increased both the sucrase and transferase component activities of S. mutans Gtf-B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using anti-Gtf-B antibody verified the interaction of rAbpA and amylase with Gtf-B. A S. gordonii abpA-deficient mutant showed greater biofilm growth under static conditions than wild-type in the presence of sucrose. Interestingly, biofilm formation by every strain was inhibited in the presence of saliva.
Conclusion: The results suggest that an extracellular protein network of AbpA-amylase-Gtf may influence the ecology of oral biofilms, likely during initial phases of colonization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amylase-binding protein B of Streptococcus gordonii is an extracellular dipeptidyl-peptidase.Infect Immun. 2008 Oct;76(10):4530-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00186-08. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18678669 Free PMC article.
-
Amylase-binding proteins A (AbpA) and B (AbpB) differentially affect colonization of rats' teeth by Streptococcus gordonii.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 Sep;149(Pt 9):2653-2660. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26022-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 12949189
-
Role of Streptococcus gordonii amylase-binding protein A in adhesion to hydroxyapatite, starch metabolism, and biofilm formation.Infect Immun. 2001 Nov;69(11):7046-56. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.7046-7056.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11598080 Free PMC article.
-
Biology of Streptococcus mutans-derived glucosyltransferases: role in extracellular matrix formation of cariogenic biofilms.Caries Res. 2011;45(1):69-86. doi: 10.1159/000324598. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Caries Res. 2011. PMID: 21346355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of inhibiting glucosyltransferases for biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutans.Int J Oral Sci. 2021 Sep 30;13(1):30. doi: 10.1038/s41368-021-00137-1. Int J Oral Sci. 2021. PMID: 34588414 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Surface Effect of Nano-Roughened Yttria-Doped Zirconia on Salivary Protein Adhesion.Materials (Basel). 2021 Oct 26;14(21):6412. doi: 10.3390/ma14216412. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771939 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfated vizantin causes detachment of biofilms composed mainly of the genus Streptococcus without affecting bacterial growth and viability.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Nov 25;20(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-02033-w. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33238885 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Salivary IgA, Amylase, Lactoferrin, and Lysozyme Before and After Comprehensive Dental Treatment in Children: A Prospective Study.Contemp Clin Dent. 2017 Oct-Dec;8(4):526-530. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_103_17. Contemp Clin Dent. 2017. PMID: 29326501 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of starch and amylase on the expression of amylase-binding protein A in Streptococcus gordonii.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012 Aug;27(4):284-94. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2012.00644.x. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22759313 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome difference among the salivary proteins adsorbed onto metallic orthodontic brackets and hydroxyapatite discs.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 28;16(7):e0254909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254909. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34319997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scannapieco FA. Saliva-bacterium interactions in oral microbial ecology. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1994;5:203–248. - PubMed
-
- Douglas CWI. Bacterial-protein interactions in the oral cavity. Adv Dent Res. 1994;8:254–262. - PubMed
-
- Rudney JD. Saliva and dental plaque. Adv Dent Res. 2000;14:29–39. - PubMed
-
- Scannapieco FA, Torres G, Levine MJ. Salivary α-amylase: role in dental plaque and caries formation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993;4:301–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

