Structural and functional definition of the specificity of a novel caspase-3 inhibitor, Ac-DNLD-CHO
- PMID: 17594508
- PMCID: PMC1931592
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-7-8
Structural and functional definition of the specificity of a novel caspase-3 inhibitor, Ac-DNLD-CHO
Abstract
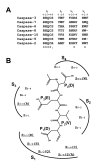
Background: The rational design of peptide-based specific inhibitors of the caspase family members using their X-ray crystallographies is an important strategy for chemical knockdown to define the critical role of each enzyme in apoptosis and inflammation. Recently, we designed a novel potent peptide inhibitor, Ac-DNLD-CHO, for caspase-3 using a new computational screening system named the Amino acid Positional Fitness (APF) method (BMC Pharmacol. 2004, 4:7). Here, we report the specificity of the DNLD sequence against caspase-3 over other major caspase family members that participate in apoptosis by computational docking and site-directed mutagenesis studies.
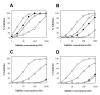
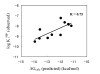
Results: Ac-DNLD-CHO inhibits caspases-3, -7, -8, and -9 activities with Kiapp values of 0.68, 55.7, >200, and >200 nM, respectively. In contrast, a well-known caspase-3 inhibitor, Ac-DEVD-CHO, inhibits all these caspases with similar Kiapp values. The selective recognition of a DNLD sequence by caspase-3 was confirmed by substrate preference studies using fluorometric methylcoumarin-amide (MCA)-fused peptide substrates. The bases for its selectivity and potency were assessed on a notable interaction between the substrate Asn (N) and the caspase-3 residue Ser209 in the S3 subsite and the tight interaction between the substrate Leu (L) and the caspase-3 hydrophobic S2 subsite, respectively, in computational docking studies. Expectedly, the substitution of Ser209 with alanine resulted in loss of the cleavage activity on Ac-DNLD-MCA and had virtually no effect on cleaving Ac-DEVD-MCA. These findings suggest that N and L residues in Ac-DNLD-CHO are the determinants for the selective and potent inhibitory activity against caspase-3.
Conclusion: On the basis of our results, we conclude that Ac-DNLD-CHO is a reliable, potent and selective inhibitor of caspase-3. The specific inhibitory effect on caspase-3 suggests that this inhibitor could become an important tool for investigations of the biological function of caspase-3. Furthermore, Ac-DNLD-CHO may be an attractive lead compound to generate novel effective non-peptidic pharmaceuticals for caspase-mediated apoptosis diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders and viral infection diseases.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A novel method for evaluation and screening of caspase inhibitory peptides by the amino acid positional fitness score.BMC Pharmacol. 2004 May 22;4:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-4-7. BMC Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15154972 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of S2-S4 specificity pockets of executioner caspase-7 revealed by structural and kinetic analysis.FEBS J. 2007 Sep;274(18):4752-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05994.x. Epub 2007 Aug 14. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 17697120
-
Structure-based discovery of a novel non-peptidic small molecular inhibitor of caspase-3.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 May 1;16(9):4854-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.03.046. Epub 2008 Mar 21. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18387304
-
Caspase inhibitors: a review of recently patented compounds (2013-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Jan;28(1):47-59. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2017.1378426. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018. PMID: 28885866 Review.
-
A small molecule inhibitor of Caspase 1.2010 Feb 25 [updated 2011 Mar 3]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2010 Feb 25 [updated 2011 Mar 3]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 21735610 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
α-Mangostin extracted from the pericarp of the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana Linn) reduces tumor growth and lymph node metastasis in an immunocompetent xenograft model of metastatic mammary cancer carrying a p53 mutation.BMC Med. 2011 Jun 3;9:69. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-69. BMC Med. 2011. PMID: 21639868 Free PMC article.
-
Low levels of Caspase-3 predict favourable response to 5FU-based chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer: Caspase-3 inhibition as a therapeutic approach.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Feb 4;7(2):e2087. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.7. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 26844701 Free PMC article.
-
Raloxifene inhibits tumor growth and lymph node metastasis in a xenograft model of metastatic mammary cancer.BMC Cancer. 2010 Oct 19;10:566. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-566. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20958960 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Death Defying Domain in Met entraps the active site of caspase-3 and blocks apoptosis in hepatocytes.Hepatology. 2014 May;59(5):2010-21. doi: 10.1002/hep.26769. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 24122846 Free PMC article.
-
Altered apoptotic responses in neurons lacking RhoB GTPase.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Dec;34(11):1737-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07891.x. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22098422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arends MJ, Wyllie AH. Apoptosis: mechanisms and roles in pathology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:223–254. - PubMed
-
- Tanuma S. Molecular mechanics of apoptosis. In: Sluyser M, editor. Apoptosis in Normal Development and Cancer. London, Taylor & Francis; 1996. pp. 39–59.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

