Expression levels of the JAK/STAT pathway in the transition from hormone-sensitive to hormone-refractory prostate cancer
- PMID: 17595657
- PMCID: PMC2360337
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603871
Expression levels of the JAK/STAT pathway in the transition from hormone-sensitive to hormone-refractory prostate cancer
Abstract
The main cause of prostate cancer-related mortality is the development of hormone-refractory disease. Circulating serum levels of IL-6 are raised in hormone-refractory prostate cancer patients and evidence from cell line studies suggests that the IL-6R/JAK/STAT3 pathway may be involved in development of this disease. In the current study we investigate if expression levels of these family members are implicated in the development of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Immunohistochemistry using IL-6R, JAK1, STAT3, pSTAT3(Tyr705) and pSTAT3(Ser727) antibodies was performed on 50 matched hormone-sensitive and hormone-refractory tumours pairs. An increase in expression of cytoplasmic IL-6 receptor, with the development of hormone-refractory prostate cancer was associated with reduced time to relapse (P=0.0074) while an increase in expression of cytoplasmic pSTAT3(Tyr705) was associated with reduced patient survival (P=0.0003). In addition, those patients with high expression of cytoplasmic pSTAT3(Tyr705) in their hormone-refractory tumours had significantly shorter time to death from biochemical relapse and overall survival in comparison to those patients with low expression of cytoplasmic pSTAT3(Tyr705) (P=0.002 and P=0.0027, respectively). Activation of STAT3, via phosphorylation is associated with reduced patient survival, suggesting that activation of the IL-6R/JAK/STAT3 pathway is involved with development of hormone-refractory prostate cancer.
Figures
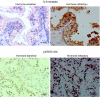
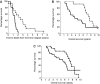
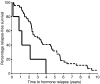
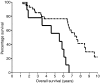
References
-
- Barton BE, Karras JG, Murphy TF, Barton A, Huang HFS (2004) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation in prostate cancer: direct STAT3 inhibition induces apoptosis in prostate cancer lines. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 11–20 - PubMed
-
- Beemsterboer PMM, de Koning HJ, Birnie E, van der Maas PJ, Schroder FH (1999) Advanced prostate cancer: course, care, and cost implications. Prostate 40: 97–104 - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Guschin D, Rogers NC, Watling D, Muller M, Horn F, Heinrich P, Stark GR, Kerr IM (1996a) JAKs, STATs and signal transduction in response to the interferons and other cytokines. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 351: 167–171 - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Kohlhuber F, Muller M (1996b) JAKs and STATs branch out. Trends Cell Biol 6: 336–340 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

