Human MUC4 mucin induces ultra-structural changes and tumorigenicity in pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 17595659
- PMCID: PMC2360313
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603868
Human MUC4 mucin induces ultra-structural changes and tumorigenicity in pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
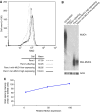
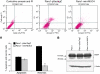
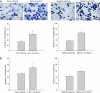
MUC4 is a type-1 transmembrane glycoprotein and is overexpressed in many carcinomas. It is a heterodimeric protein of 930 kDa, composed of a mucin-type subunit, MUC4alpha, and a membrane-bound growth factor-like subunit, MUC4beta. MUC4 mRNA contains unique 5' and 3' coding sequences along with a large variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) domain of 7-19 kb. A direct association of MUC4 overexpression has been established with the degree of invasiveness and poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer. To understand the precise role of MUC4 in pancreatic cancer, we engineered a MUC4 complementary DNA construct, mini-MUC4, whose deduced protein (320 kDa) is comparable with that of wild-type MUC4 (930 kDa) but represents only 10% of VNTR. Stable ectopic expression of mini-MUC4 in two human pancreatic cancer cell lines, Panc1 and MiaPaCa, showed that MUC4 minigene expression follows a biosynthesis and localisation pattern similar to the wild-type MUC4. Expression of MUC4 resulted in increased growth, motility, and invasiveness of the pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Ultra-structural examination of MUC4-transfected cells showed the presence of increased number and size of mitochondria. The MUC4-expressing cells also demonstrated an enhanced tumorigenicity in an orthotopic xenograft nude mice model, further supporting a direct role of MUC4 in inducing the cancer properties. In conclusion, our results suggest that MUC4 promotes tumorigenicity and is directly involved in growth and survival of the cancer cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MUC4 mucin potentiates pancreatic tumor cell proliferation, survival, and invasive properties and interferes with its interaction to extracellular matrix proteins.Mol Cancer Res. 2007 Apr;5(4):309-20. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0353. Epub 2007 Apr 3. Mol Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17406026
-
Alternate splicing at the 3'-end of the human pancreatic tumor-associated mucin MUC4 cDNA.Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 2001;21(1):83-96. doi: 10.1002/1520-6866(2001)21:1<83::aid-tcm8>3.0.co;2-3. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 2001. PMID: 11135323
-
Human MUC4 mucin cDNA and its variants in pancreatic carcinoma.J Biochem. 2000 Aug;128(2):233-43. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022746. J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10920259
-
Emerging roles of MUC4 in cancer: a novel target for diagnosis and therapy.Cancer Res. 2007 Jan 15;67(2):433-6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3114. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17234748 Review.
-
MUC4 mucin- a therapeutic target for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Jul;21(7):657-669. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1323880. Epub 2017 May 29. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28460571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-induced oxidative stress promotes MUC4 degradation via autophagy to enhance pancreatic cancer cells survival.Oncogene. 2016 Nov 10;35(45):5882-5892. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.119. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27109098 Free PMC article.
-
MUC4, a novel immunohistochemical marker identified by gene expression profiling, differentiates pleural sarcomatoid mesothelioma from lung sarcomatoid carcinoma.Mod Pathol. 2017 May;30(5):672-681. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2016.181. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Mod Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28128276
-
Recent progress on normal and malignant pancreatic stem/progenitor cell research: therapeutic implications for the treatment of type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus and aggressive pancreatic cancer.Gut. 2008 Oct;57(10):1456-68. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.150052. Gut. 2008. PMID: 18791122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, evolution, and biology of the MUC4 mucin.FASEB J. 2008 Apr;22(4):966-81. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9673rev. Epub 2007 Nov 16. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18024835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mucin MUC4 and its membrane partner ErbB2 regulate biological properties of human CAPAN-2 pancreatic cancer cells via different signalling pathways.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032232. Epub 2012 Feb 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22393391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alos L, Lujan B, Castillo M, Nadal A, Carreras M, Caballero M, de BC, Cardesa A (2005) Expression of membrane-bound mucins (MUC1 and MUC4) and secreted mucins (MUC2, MUC5AC, MUC5B, MUC6 and MUC7) in mucoepidermoid carcinomas of salivary glands. Am J Surg Pathol 29: 806–813 - PubMed
-
- Andrianifahanana M, Agrawal A, Singh AP, Moniaux N, Van SI, Aubert JP, Meza J, Batra SK (2005) Synergistic induction of the MUC4 mucin gene by interferon-gamma and retinoic acid in human pancreatic tumour cells involves a reprogramming of signalling pathways. Oncogene 24: 6143–6154 - PubMed
-
- Andrianifahanana M, Moniaux N, Schmied BM, Ringel J, Friess H, Hollingsworth MA, Buchler MW, Aubert JP, Batra SK (2001) Mucin (MUC) gene expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis: a potential role of MUC4 as a tumor marker of diagnostic significance. Clin Cancer Res 7: 4033–4040 - PubMed
-
- Audie JP, Janin A, Porchet N, Copin MC, Gosselin B, Aubert JP (1993) Expression of human mucin genes in respiratory, digestive, and reproductive tracts ascertained by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem 41: 1479–1485 - PubMed
-
- Audie JP, Tetaert D, Pigny P, Buisine MP, Janin A, Aubert JP, Porchet N, Boersma A (1995) Mucin gene expression in the human endocervix. Hum Reprod 10: 98–102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

