Novel antiangiogenic pathway of thrombospondin-1 mediated by suppression of the cell cycle
- PMID: 17596205
- PMCID: PMC11159057
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00534.x
Novel antiangiogenic pathway of thrombospondin-1 mediated by suppression of the cell cycle
Abstract
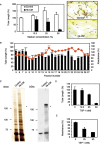
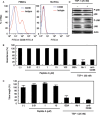
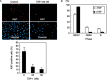
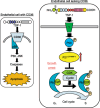
We have recently reported that keratin 14-promoter-driven vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-E(NZ-7) transgenic mice have a significant number of capillary vessels in subcutaneous tissue. However, these vessels are generated in a layer some distance from the epithelial basal cells that express VEGF-E(NZ-7), suggesting that one or more antiangiogenenic molecules may exist very near the basal cell layer. By screening keratinocyte-conditioned medium, we found that thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) is produced from keratinocytes and suppresses human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) growth as well as tubular formation in a HUVEC-fibroblast coculture system. Different to the known mechanism of CD36-dependent endothelial cell apoptosis, the HUVEC we used did not express CD36 at detectable levels, indicating a new mechanism for TSP-1-induced antiangiogenesis. We found that TSP-1 induces little apoptosis of endothelial cells but causes cell-cycle arrest, increasing the amounts of p21(CIP/WAF-1) and unphosphorylated retinoblastoma (Rb) in HUVEC. CD36-binding peptide in TSP-1 and CD36-neutralizing antibody did not block the TSP-1-induced cell-cycle arrest. Our results strongly suggest that TSP-1 utilizes a novel pathway for its antiangiogenic effect independent of CD36, and suppresses the cell cycle.
Figures

References
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Eng J Med 1991; 285: 1182–6. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Folkman J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996; 86: 353–64. - PubMed
-
- Risau W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997; 386: 671–4. - PubMed
-
- Kiba A, Sagara H, Hara T, Shibuya M. VEGFR‐2‐specific ligand VEGF‐E induces non‐edematous hyper‐vascularization in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 301: 371–7. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors. APMIS 2004; 112: 496–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

