Vaccine platform for prevention of tuberculosis and mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through breastfeeding
- PMID: 17596303
- PMCID: PMC1951420
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00707-07
Vaccine platform for prevention of tuberculosis and mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through breastfeeding
Abstract
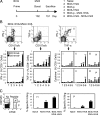
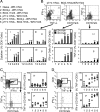
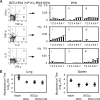
Most children in Africa receive their vaccine against tuberculosis at birth. Those infants born to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-positive mothers are at high risk of acquiring HIV-1 infection through breastfeeding in the first weeks of their lives. Thus, the development of a vaccine which would protect newborns against both of these major global killers is a logical yet highly scientifically, ethically, and practically challenging aim. Here, a recombinant lysine auxotroph of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG), a BCG strain that is safer than those currently used and expresses an African HIV-1 clade-derived immunogen, was generated and shown to be stable and to induce durable, high-quality HIV-1-specific CD4(+)- and CD8(+)-T-cell responses. Furthermore, when the recombinant BCG vaccine was used in a priming-boosting regimen with heterologous components, the HIV-1-specific responses provided protection against surrogate virus challenge, and the recombinant BCG vaccine alone protected against aerosol challenge with M. tuberculosis. Thus, inserting an HIV-1-derived immunogen into the scheduled BCG vaccine delivered at or soon after birth may prime HIV-1-specific responses, which can be boosted by natural exposure to HIV-1 in the breast milk and/or by a heterologous vaccine such as recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara delivering the same immunogen, and decrease mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 during breastfeeding.
Figures



References
-
- Adkins, B., C. Leclerc, and S. Marshall-Clarke. 2004. Neonatal adaptive immunity comes of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:553-564. - PubMed
-
- Alter, G., J. M. Malenfant, and M. Altfeld. 2004. CD107a as a functional marker for the identification of natural killer cell activity. J. Immunol. Methods 294:15-22. - PubMed
-
- Ami, Y., Y. Izumi, K. Matsuo, K. Someya, M. Kanekiyo, S. Horibata, N. Yoshino, K. Sakai, K. Shinohara, S. Matsumoto, T. Yamada, S. Yamazaki, N. Yamamoto, and M. Honda. 2005. Priming-boosting vaccination with recombinant Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin and a nonreplicating vaccinia virus recombinant leads to long-lasting and effective immunity. J. Virol. 79:12871-12879. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersson, G. E., and P. M. Sharp. 1996. Codon usage in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Microbiology 142:915-925. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

