Insight into redox-regulated gene networks in vascular cells
- PMID: 17597926
- PMCID: PMC1896051
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630001379
Insight into redox-regulated gene networks in vascular cells
Abstract
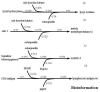
To understand the complex nature of the atherogenic response initiated by oxidative stress in vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs), computational prediction methodology was employed to define putative gene-gene and gene-environment interactions in vSMCs subjected to oxidative chemical stress. Computational relationships were derived from the global gene expression profiles of murine cells challenged with a chemical pro-oxidant to cause oxidative stress or cells treated with anti-oxidant prior to oxidative injury. Target clones were chosen based on their biological relevance within the context of the atherogenic response and included lysyl oxidase, matrix metalloproteinase 2, insulin like growth factor binding protein 5, and lymphocyte antigen 6c. Established biological relationships were derived computationally confirming the usefulness of the algorithm in uncovering novel biological relationships worthy of future investigation. Thus, the predictive algorithm can be a useful tool to advance the frontiers of biological discovery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic profiles and predictive biological networks in oxidant-induced atherogenesis.Physiol Genomics. 2003 May 13;13(3):263-75. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00006.2003. Epub 2003 May 13. Physiol Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12657712
-
Identification of albumin precursor protein, Phi AP3, and alpha-smooth muscle actin as novel components of redox sensing machinery in vascular smooth muscle cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2002 May;61(5):1174-83. doi: 10.1124/mol.61.5.1174. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11961136
-
Paracrine signalling from monocytes enables desirable extracellular matrix accumulation and temporally appropriate phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cell-like cells derived from adipose stromal cells.Acta Biomater. 2020 Feb;103:129-141. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.12.006. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 31821896
-
Phenotypic Modulation of Macrophages and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis-Nitro-Redox Interconnections.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 26;10(4):516. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040516. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33810295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relations between metabolic syndrome, oxidative stress and inflammation and cardiovascular disease.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2008;70(3):193-219. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2008. PMID: 18669160 Review.
Cited by
-
The innate immune response to ischemic injury: a multiscale modeling perspective.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Apr 10;12(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0580-z. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29631571 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative injury is a common consequence of BMPR2 mutations.Pulm Circ. 2011;1(1):72-83. doi: 10.4103/2045-8932.78107. Pulm Circ. 2011. PMID: 21904662 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Lysyl Oxidases in the Cardiovascular System: New Concepts and Therapeutic Challenges.Biomolecules. 2019 Oct 14;9(10):610. doi: 10.3390/biom9100610. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31615160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling genetic regulatory networks of mammalian retroelements.BMC Proc. 2009 Mar 10;3 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S3. doi: 10.1186/1753-6561-3-s2-s3. BMC Proc. 2009. PMID: 19278559 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
