Ranking and averaging independent component analysis by reproducibility (RAICAR)
- PMID: 17598162
- PMCID: PMC6870671
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20432
Ranking and averaging independent component analysis by reproducibility (RAICAR)
Abstract
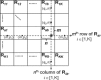
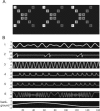
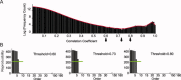
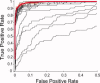
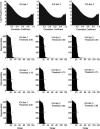
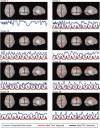
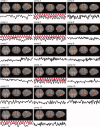
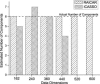
Independent component analysis (ICA) is a data-driven approach that has exhibited great utility for functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Standard ICA implementations, however, do not provide the number and relative importance of the resulting components. In addition, ICA algorithms utilizing gradient-based optimization give decompositions that are dependent on initialization values, which can lead to dramatically different results. In this work, a new method, RAICAR (Ranking and Averaging Independent Component Analysis by Reproducibility), is introduced to address these issues for spatial ICA applied to fMRI. RAICAR utilizes repeated ICA realizations and relies on the reproducibility between them to rank and select components. Different realizations are aligned based on correlations, leading to aligned components. Each component is ranked and thresholded based on between-realization correlations. Furthermore, different realizations of each aligned component are selectively averaged to generate the final estimate of the given component. Reliability and accuracy of this method are demonstrated with both simulated and experimental fMRI data.
Copyright 2007 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparing the reliability of different ICA algorithms for fMRI analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 27;17(6):e0270556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270556. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35759502 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of fMRI data by blind separation into independent spatial components.Hum Brain Mapp. 1998;6(3):160-88. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(1998)6:3<160::AID-HBM5>3.0.CO;2-1. Hum Brain Mapp. 1998. PMID: 9673671 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Generalized RAICAR: discover homogeneous subject (sub)groups by reproducibility of their intrinsic connectivity networks.Neuroimage. 2012 Oct 15;63(1):403-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.060. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22789741
-
Study of temporal stationarity and spatial consistency of fMRI noise using independent component analysis.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005 Jun;24(6):712-8. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2005.846852. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005. PMID: 15957595 Clinical Trial.
-
Extracting functional networks with spatial independent component analysis: the role of dimensionality, reliability and aggregation scheme.Curr Opin Neurol. 2011 Aug;24(4):378-85. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e32834897a5. Curr Opin Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21734575 Review.
Cited by
-
An open science resource for establishing reliability and reproducibility in functional connectomics.Sci Data. 2014 Dec 9;1:140049. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2014.49. eCollection 2014. Sci Data. 2014. PMID: 25977800 Free PMC article.
-
DisConICA: a Software Package for Assessing Reproducibility of Brain Networks and their Discriminability across Disorders.Neuroinformatics. 2020 Jan;18(1):87-107. doi: 10.1007/s12021-019-09422-1. Neuroinformatics. 2020. PMID: 31187352 Free PMC article.
-
Mutual information spectrum for selection of event-related spatial components. Application to eloquent motor cortex mapping.Front Neuroinform. 2014 Jan 20;7:53. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2013.00053. eCollection 2013. Front Neuroinform. 2014. PMID: 24478692 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale sparse functional networks from resting state fMRI.Neuroimage. 2017 Aug 1;156:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 5. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 28483721 Free PMC article.
-
Brain network informed subject community detection in early-onset schizophrenia.Sci Rep. 2014 Jul 3;4:5549. doi: 10.1038/srep05549. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24989351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckmann CF, Smith SM ( 2004): Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23: 137–152. - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS ( 1995): Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo‐planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34: 537–541. - PubMed
-
- Catalan MJ, Honda M, Weeks RA, Cohen LG, Hallett M ( 1998): The functional neuroanatomy of simple and complex sequential finger movements: A PET study. Brain 121: 253–264. - PubMed
-
- Cox RW ( 1996): AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res 29: 162–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

