The mirtron pathway generates microRNA-class regulatory RNAs in Drosophila
- PMID: 17599402
- PMCID: PMC2729315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.028
The mirtron pathway generates microRNA-class regulatory RNAs in Drosophila
Abstract
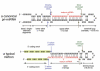
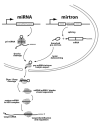
The canonical microRNA (miRNA) pathway converts primary hairpin precursor transcripts into approximately 22 nucleotide regulatory RNAs via consecutive cleavages by two RNase III enzymes, Drosha and Dicer. In this study, we characterize Drosophila small RNAs that derive from short intronic hairpins termed "mirtrons." Their nuclear biogenesis appears to bypass Drosha cleavage, which is essential for miRNA biogenesis. Instead, mirtron hairpins are defined by the action of the splicing machinery and lariat-debranching enzyme, which yield pre-miRNA-like hairpins. The mirtron pathway merges with the canonical miRNA pathway during hairpin export by Exportin-5, and both types of hairpins are subsequently processed by Dicer-1/loqs. This generates small RNAs that can repress perfectly matched and seed-matched targets, and we provide evidence that they function, at least in part, via the RNA-induced silencing complex effector Ago1. These findings reveal that mirtrons are an alternate source of miRNA-type regulatory RNAs.
Figures





References
-
- Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006;13:1097–1101. - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Rajewsky N. The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Conklin JF, Goldman A, Lopez AJ. Stabilization and analysis of intron lariats in vivo. Methods. 2005;37:368–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

