Lateral hypothalamic orexin neurons are critically involved in learning to associate an environment with morphine reward
- PMID: 17599478
- PMCID: PMC2030620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2007.05.025
Lateral hypothalamic orexin neurons are critically involved in learning to associate an environment with morphine reward
Abstract
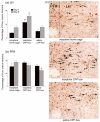
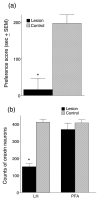
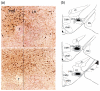
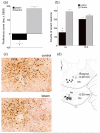
Previously, we reported that lateral hypothalamic (LH) orexin neurons are stimulated in proportion to the preference shown for reward-associated cues during conditioned place preference (CPP) testing. Here, we examine for the first time the role of these neurons in the acquisition of morphine CPP. Results show that LH orexin neurons, but not those in the perifornical area (PFA), are stimulated during conditioning when morphine is given in a novel drug-paired environment (CPP compartment) but not when given in the home cage, nor when saline was given in the CPP environment. Furthermore, bilateral excitotoxic lesions of the LH orexin area completely blocked the acquisition of morphine CPP. Lesions that spared LH orexin neurons had no effect. Orexin neurons in the LH project to the ventral tegmental area (VTA), an area important in the acquisition of morphine CPP. Therefore, we investigated the importance of the LH orexin connection to the VTA in the acquisition of a morphine CPP using a disconnection technique involving a unilateral excitotoxic lesion of LH orexin neurons and contralateral blockade of VTA orexin receptors. Results indicated that a unilateral LH orexin lesion together with a microinjection of the orexin A antagonist (SB 334867) into the contralateral VTA prior to each morphine-pairing session was sufficient to block the development of a morphine CPP. Either of these treatments by themselves was not sufficient to block CPP development. These results demonstrate the importance of LH orexin neurons and their projections to the VTA in the formation of associations between environmental cues and drug reward.
Figures
References
-
- Baldo BA, Gual-Bonilla L, Sijapati K, Daniel RA, Landry CF, Kelley AE. Activation of a subpopulation of orexin/hypocretin-containing hypothalamic neurons by GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition of the nucleus accumbens shell, but not by exposure to a novel environment. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19:376–386. - PubMed
-
- Borgland SL, Taha SA, Sarti F, Fields HL, Bonci A. Orexin A in the VTA is critical for the induction of synaptic plasticity and behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Neuron. 2006;49:589–601. - PubMed
-
- Cavalcante-Lima HR, Lima HR, Costa-e-Sousa RH, Olivares EL, Cedraz-Mercez PL, Reis RO, Badaue-Passos D, Jr., De-Lucca W, Jr., de Medeiros MA, Cortes Wda S, Reis LC. Dipsogenic stimulation in ibotenic DRN-lesioned rats induces concomitant sodium appetite. Neurosci Lett. 2005;374:5–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

