Implementing Single Source: the STARBRITE proof-of-concept study
- PMID: 17600107
- PMCID: PMC1975790
- DOI: 10.1197/jamia.M2157
Implementing Single Source: the STARBRITE proof-of-concept study
Abstract
Objective: Inefficiencies in clinical trial data collection cause delays, increase costs, and may reduce clinician participation in medical research. In this proof-of-concept study, we examine the feasibility of using point-of-care data capture for both the medical record and clinical research in the setting of a working clinical trial. We hypothesized that by doing so, we could increase reuse of patient data, eliminate redundant data entry, and minimize disruption to clinic workflow.
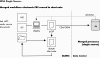
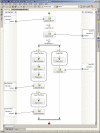
Design: We developed and used a point-of-care electronic data capture system to record data during patient visits. The standards-based system was used for clinical research and to generate the clinic note for the medical record. The system worked in parallel with data collection procedures already in place for an ongoing multicenter clinical trial. Our system was iteratively designed after analyzing case report forms and clinic notes, and observing clinic workflow patterns and business procedures. Existing data standards from CDISC and HL7 were used for database insertion and clinical document exchange.
Results: Our system was successfully integrated into the clinic environment and used in two live test cases without disrupting existing workflow. Analyses performed during system design yielded detailed information on practical issues affecting implementation of systems that automatically extract, store, and reuse healthcare data.
Conclusion: Although subject to the limitations of a small feasibility study, our study demonstrates that electronic patient data can be reused for prospective multicenter clinical research and patient care, and demonstrates a need for further development of therapeutic area standards that can facilitate researcher use of healthcare data.
Figures





References
-
- Justice AC, Erdos J, Brandt C, Conigliaro J, Tierney W, Bryant K. The Veterans Affairs Healthcare System Med Care 2006;44(S8). - PubMed
-
- Jordan K, Porcheret M, Kadam UT, Croft P. Use of general practice consultation databases in rheumatology research Rheumatol 2006;45:126-128. - PubMed
-
- Lusignan S, van Weel C. The use of routinely collected computer data for research in primary care: opportunities and challenges Fam Pract 2005;23:253-263. - PubMed
-
- Hellings P. A rich source of clinical research data: medical records and telephone logs J Pediatr Health Care 2004;18:154-155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

