Solution structure of the general transcription factor 2I domain in mouse TFII-I protein
- PMID: 17600150
- PMCID: PMC2203370
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.072792007
Solution structure of the general transcription factor 2I domain in mouse TFII-I protein
Abstract
The general transcription factor TFII-I, with the corresponding gene name GTF2I, is an unusual transcriptional regulator that associates with both basal and signal-induced transcription factors. TFII-I consists of six GTF2I repeat domains, called I-repeats R1-R6. The structure and function of the GTF2I domain are not clearly understood, even though it contains a helix-loop-helix motif, which is considered to be the protein-protein interaction area, based on biochemical analyses. Here, we report the solution structure of the fifth repeat of the six GTF2I repeat domains from murine TFII-I, which was determined by heteronuclear multidimensional NMR spectroscopy (PDB code 1Q60). The three-dimensional structure of the GTF2I domain is classified as a new fold, consisting of four helices (residues 8-24, 34-39, 63-71, and 83-91), two antiparallel beta strands (residues 44-47 and 77-80), and a well-defined loop containing two beta-turns between sheet 1 and helix 3. All of the repeats probably have similar folds to that of repeat 5, because the conserved residues in the GTF2I repeat domains are assembled on the hydrophobic core, turns, and secondary structure elements, as revealed by a comparison of the sequences of the first through the sixth GTF2I repeats in TFII-I.
Figures

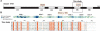
References
-
- Bax A. 1994. Multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance methods for protein studies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 4: 738–744.
-
- Casteel D.E., Zhuang, S., Gudi, T., Tang, J., Vuica, M., Desiderio, S., and Pilz, R.S. 2002. cGMP-dependent protein kinase Iβ physically and functionally interacts with the transcriptional regulator TFII-I. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 32003–32014. - PubMed
-
- Cavanagh J., Fairbrother, W.J., Palmer III, A.G., and Skelton, N.J. 1996. Protein NMR spectroscopy, principles and practice. Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
-
- Cheriyath V. and Roy, A.L. 2001. Structure–function analysis of TFII-I. Roles of the N-terminal end, basic resion, and I-repeat. J. Biochem. 276: 8377–8383. - PubMed
-
- Cheriyath V., Desgranges, Z.P., and Roy, A.L. 2002. c-Src-dependent transcriptional activation of TFII-I. J. Biol. Chem. 277: 22798–22805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

