Analysis of septins across kingdoms reveals orthology and new motifs
- PMID: 17601340
- PMCID: PMC1931588
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-103
Analysis of septins across kingdoms reveals orthology and new motifs
Abstract
Background: Septins are cytoskeletal GTPase proteins first discovered in the fungus Saccharomyces cerevisiae where they organize the septum and link nuclear division with cell division. More recently septins have been found in animals where they are important in processes ranging from actin and microtubule organization to embryonic patterning and where defects in septins have been implicated in human disease. Previous studies suggested that many animal septins fell into independent evolutionary groups, confounding cross-kingdom comparison.
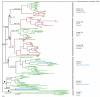
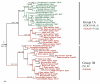
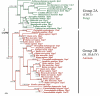
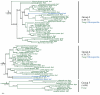
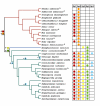
Results: In the current work, we identified 162 septins from fungi, microsporidia and animals and analyzed their phylogenetic relationships. There was support for five groups of septins with orthology between kingdoms. Group 1 (which includes S. cerevisiae Cdc10p and human Sept9) and Group 2 (which includes S. cerevisiae Cdc3p and human Sept7) contain sequences from fungi and animals. Group 3 (which includes S. cerevisiae Cdc11p) and Group 4 (which includes S. cerevisiae Cdc12p) contain sequences from fungi and microsporidia. Group 5 (which includes Aspergillus nidulans AspE) contains sequences from filamentous fungi. We suggest a modified nomenclature based on these phylogenetic relationships. Comparative sequence alignments revealed septin derivatives of already known G1, G3 and G4 GTPase motifs, four new motifs from two to twelve amino acids long and six conserved single amino acid positions. One of these new motifs is septin-specific and several are group specific.
Conclusion: Our studies provide an evolutionary history for this important family of proteins and a framework and consistent nomenclature for comparison of septin orthologs across kingdoms.
Figures
References
-
- De Virgilio C, DeMarini DJ, Pringle JR. SPR28, a sixth member of the septin gene family in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that is expressed specifically in sporulating cells. Microbiology. 1996;142 ( Pt 10):2897–2905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

