Central kappa-opioid receptor-mediated antidepressant-like effects of nor-Binaltorphimine: behavioral and BDNF mRNA expression studies
- PMID: 17601558
- PMCID: PMC2031926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.045
Central kappa-opioid receptor-mediated antidepressant-like effects of nor-Binaltorphimine: behavioral and BDNF mRNA expression studies
Abstract
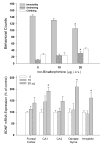
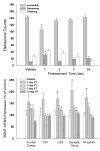
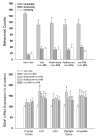
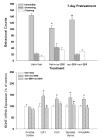
kappa-opioid receptor antagonists such as nor-Binaltorphimine (nor-BNI) have been shown to produce antidepressant-like behavioral effects in animal models of depression. The aim of this study was to investigate further the duration of centrally administered nor-BNI-induced antidepressant-like actions measured by both behavior and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene expression. In addition, antagonist studies were conducted to determine the role of opioid receptor subtypes and the time course of nor-BNI's pharmacological actions. Antidepressant-like behavioral effects were measured by decreased immobility in the rat forced swim test and BDNF mRNA expression was determined by in situ hybridization. Centrally administered nor-BNI (20 microg, i.c.v.) decreased immobility and increased BDNF mRNA expression in the hippocampus on day 1, not on days 3-14, post-administration. Systemic administration of selective mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptor antagonists did not block nor-BNI-induced antidepressant-like effects. In contrast, i.c.v. administration of nor-BNI 7 or 14 days earlier significantly blocked subsequent nor-BNI-induced decreased immobility and upregulation of BDNF mRNA expression. Although the duration of nor-BNI's antidepressant-like effects did not synchronize with that of its kappa-opioid receptor antagonist effects, this study is the first to show that centrally administered nor-BNI, like most clinically used antidepressants, can upregulate BDNF mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus. These findings further demonstrate that central kappa-opioid receptor mediates antidepressant-like effects of nor-BNI measured by both behavior and BDNF gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endogenous opioids upregulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA through delta- and micro-opioid receptors independent of antidepressant-like effects.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Feb;23(4):984-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04621.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16519663 Free PMC article.
-
The delta-opioid receptor agonist (+)BW373U86 regulates BDNF mRNA expression in rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004 Apr;29(4):649-59. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300345. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004. PMID: 14647482
-
Peptidic delta opioid receptor agonists produce antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test and regulate BDNF mRNA expression in rats.Brain Res. 2006 Jan 19;1069(1):172-81. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.11.005. Epub 2005 Dec 20. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16364263 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic administration of the delta opioid receptor agonist (+)BW373U86 and antidepressants on behavior in the forced swim test and BDNF mRNA expression in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Nov;183(1):31-40. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0113-5. Epub 2005 Oct 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 16220339 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and serotonergic consequences of decreasing or increasing hippocampus brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Nov;55(6):1006-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18761360 Review.
Cited by
-
Zyklophin, a systemically active selective kappa opioid receptor peptide antagonist with short duration of action.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 27;106(43):18396-401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910180106. Epub 2009 Oct 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19841255 Free PMC article.
-
Addiction to prescription opioids: characteristics of the emerging epidemic and treatment with buprenorphine.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008 Oct;16(5):435-41. doi: 10.1037/a0013637. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18837640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Monoamines-Novel Targets for Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015;13(5):636-55. doi: 10.2174/1570159x13666150630175044. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26467412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure selectivity relationship studies of 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6β-[(4'-pyridyl)carboxamido]morphinan derivatives toward the development of the mu opioid receptor antagonists.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Sep 15;21(18):5625-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.06.135. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21788135 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid Mechanisms and the Treatment of Depression.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2024;66:67-99. doi: 10.1007/7854_2023_448. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37923934 Review.
References
-
- Bramham CR, Messaoudi E. BDNF function in adult synaptic plasticity: the synaptic consolidation hypothesis. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;76:99–125. - PubMed
-
- Broom DC, Jutkiewicz EM, Folk JE, Traynor JR, Rice KC, Woods JH. Nonpeptidic delta-opioid receptor agonists reduce immobility in the forced swim assay in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;26:744–755. - PubMed
-
- Butelman ER, Negus SS, Ai Y, de Costa BR, Woods JH. Kappa opioid antagonist effects of systemically administered nor-binaltorphimine in a thermal antinociception assay in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;267:1269–1276. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr, Beguin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Lee DY, Cohen BM. Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:440–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

