Effects of intranasal administration of a leptin-secreting Lactococcus lactis recombinant on food intake, body weight, and immune response of mice
- PMID: 17601816
- PMCID: PMC1950963
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00295-07
Effects of intranasal administration of a leptin-secreting Lactococcus lactis recombinant on food intake, body weight, and immune response of mice
Abstract
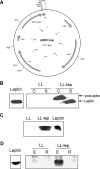
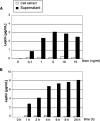
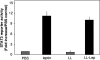
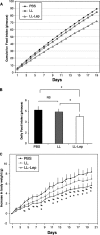
Leptin is an adipocyte-derived pleiotropic hormone that modulates a large number of physiological functions, including control of body weight and regulation of the immune system. In this work, we show that a recombinant strain of the food-grade lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis (LL-lep) can produce and efficiently secrete human leptin. The secreted leptin is a fully biologically active hormone, as demonstrated by its capacity to stimulate a STAT3 reporter gene in HEK293 cells transfected with the Ob-Rb leptin receptor. The immunomodulatory activity of leptin-secreting L. lactis was evaluated in vivo by coexpression with the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. In C57BL/6 mice immunized intranasally with a recombinant L. lactis strain coproducing leptin and E7 antigen, the adaptive immune response was significantly higher than in mice immunized with recombinant L. lactis producing only E7 antigen, demonstrating adjuvanticity of leptin. We then analyzed the effects of intranasally administered LL-lep in obese ob/ob mice. We observed that daily administration of LL-lep to these mice significantly reduced body weight gain and food intake. These results demonstrate that leptin can be produced and secreted in an active form by L. lactis and that leptin-producing L. lactis regulates in vivo antigen-specific immune responses, as well as body weight and food consumption.
Figures

References
-
- Ahima, R. S., and S. Y. Osei. 2004. Leptin signaling. Physiol. Behav. 81:223-241. - PubMed
-
- Amer, A., and T. J. Maher. 2005. Nasal administration of the calcium channel blocker diltiazem decreases food intake and attenuates weight gain in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 82:379-387. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez-Humaran, L. G., N. G. Cortes-Perez, Y. Le Loir, A. Gruss, C. Rodriguez-Padilla, O. Saucedo-Cardenas, P. Langella, and R. Montes de Oca-Luna. 2003. Fusion to a carrier protein and a synthetic propeptide enhances E7 HPV-16 production and secretion in Lactococcus lactis. Biotechnol. Prog. 19:1101-1104. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez-Humaran, L. G., N. G. Cortes-Perez, F. Lefevre, V. Guimaraes, S. Rabot, J. M. Alcocer-Gonzalez, J. J. Gratadoux, C. Rodriguez-Padilla, R. S. Tamez-Guerra, G. Corthier, A. Gruss, and P. Langella. 2005. A novel mucosal vaccine based on live Lactococci expressing E7 antigen and IL-12 induces systemic and mucosal immune responses and protects mice against human papillomavirus type 16-induced tumors. J. Immunol. 175:7297-7302. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez-Humaran, L. G., P. Langella, J. Commissaire, S. Gilbert, Y. Le Loir, R. L'Haridon, and G. Corthier. 2003. Controlled intra- or extracellular production of staphylococcal nuclease and ovine omega interferon in Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 224:307-313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

