Development of innovative pediocin PA-1 by DNA shuffling among class IIa bacteriocins
- PMID: 17601819
- PMCID: PMC1950993
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00558-07
Development of innovative pediocin PA-1 by DNA shuffling among class IIa bacteriocins
Abstract
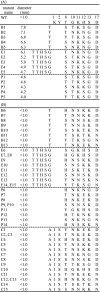
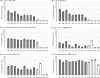
Pediocin PA-1 is a member of the class IIa bacteriocins, which show antimicrobial effects against lactic acid bacteria. To develop an improved version of pediocin PA-1, reciprocal chimeras between pediocin PA-1 and enterocin A, another class IIa bacteriocin, were constructed. Chimera EP, which consisted of the C-terminal half of pediocin PA-1 fused to the N-terminal half of enterocin A, showed increased activity against a strain of Leuconostoc lactis isolated from a sour-spoiled dairy product. To develop an even more effective version of this chimera, a DNA-shuffling library was constructed, wherein four specific regions within the N-terminal half of pediocin PA-1 were shuffled with the corresponding sequences from 10 other class IIa bacteriocins. Activity screening indicated that 63 out of 280 shuffled mutants had antimicrobial activity. A colony overlay activity assay showed that one of the mutants (designated B1) produced a >7.8-mm growth inhibition circle on L. lactis, whereas the parent pediocin PA-1 did not produce any circle. Furthermore, the active shuffled mutants showed increased activity against various species of Lactobacillus, Pediococcus, and Carnobacterium. Sequence analysis revealed that the active mutants had novel N-terminal sequences; in active mutant B1, for example, the parental pediocin PA-1 sequence (KYYGNGVTCGKHSC) was changed to TKYYGNGVSCTKSGC. These new and improved DNA-shuffled bacteriocins could prove useful as food additives for inhibiting sour spoilage of dairy products.
Figures
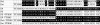
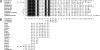
Similar articles
-
Heterologous coproduction of enterocin A and pediocin PA-1 by Lactococcus lactis: detection by specific peptide-directed antibodies.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Aug;66(8):3543-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.8.3543-3549.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10919819 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic relationships among type IIa bacteriocins: temperature effects on antimicrobial activity and on structure of the C-terminal amphipathic alpha helix as a receptor-binding region.Biochemistry. 2004 Jul 20;43(28):9009-20. doi: 10.1021/bi036018e. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15248758
-
Isolation and characterization of pediocin AcH chimeric protein mutants with altered bactericidal activity.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998 Jun;64(6):1997-2005. doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.6.1997-2005.1998. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9603806 Free PMC article.
-
Pediocin PA-1, a wide-spectrum bacteriocin from lactic acid bacteria.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2002 Mar;42(2):91-121. doi: 10.1080/10408690290825475. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2002. PMID: 11934133 Review.
-
Pediococcus spp.: An important genus of lactic acid bacteria and pediocin producers.Biotechnol Adv. 2017 May-Jun;35(3):361-374. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.03.004. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Biotechnol Adv. 2017. PMID: 28284993 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Class IIa Bacteriocins as Therapeutic Agents.Int J Microbiol. 2012;2012:386410. doi: 10.1155/2012/386410. Epub 2011 Nov 30. Int J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22187559 Free PMC article.
-
Site Mutation Improves the Expression and Antimicrobial Properties of Fungal Defense.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;12(8):1283. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12081283. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627703 Free PMC article.
-
Enterocin A mutants identified by saturation mutagenesis enhance potency towards vancomycin-resistant Enterococci.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016 Feb;113(2):414-23. doi: 10.1002/bit.25710. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016. PMID: 26191783 Free PMC article.
-
From design to screening: a new antimicrobial peptide discovery pipeline.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059305. Epub 2013 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527157 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriocins - a viable alternative to antibiotics?Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Feb;11(2):95-105. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2937. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23268227 Review.
References
-
- Abee, T., L. Krockel, and C. Hill. 1995. Bacteriocins: modes of action and potentials in food preservation and control of food poisoning. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 28:169-185. - PubMed
-
- Bhunia, A. K., M. C. Johnson, and B. Ray. 1988. Purification, characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 65:261-268. - PubMed
-
- Björkroth, K. J., R. Geisen, U. Schillinger, N. Weiss, P. De Vos, W. H. Holzapfel, H. J. Korkeala, and P. Vandamme. 2000. Characterization of Leuconostoc gasicomitatum sp. nov., associated with spoiled raw tomato-marinated broiler meat strips packaged under modified-atmosphere conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66:3764-3772. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

