The Arabidopsis MATE transporter TT12 acts as a vacuolar flavonoid/H+ -antiporter active in proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells of the seed coat
- PMID: 17601828
- PMCID: PMC1955721
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.046029
The Arabidopsis MATE transporter TT12 acts as a vacuolar flavonoid/H+ -antiporter active in proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells of the seed coat
Abstract
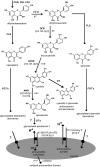
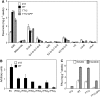
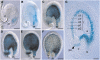
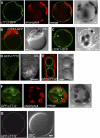
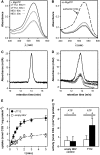
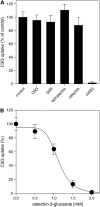
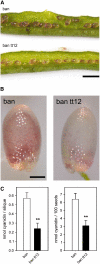
Phenotypic characterization of the Arabidopsis thaliana transparent testa12 (tt12) mutant encoding a membrane protein of the multidrug and toxic efflux transporter family, suggested that TT12 is involved in the vacuolar accumulation of proanthocyanidin precursors in the seed. Metabolite analysis in tt12 seeds reveals an absence of flavan-3-ols and proanthocyanidins together with a reduction of the major flavonol quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside. The TT12 promoter is active in cells synthesizing proanthocyanidins. Using translational fusions between TT12 and green fluorescent protein, it is demonstrated that this transporter localizes to the tonoplast. Yeast vesicles expressing TT12 can transport the anthocyanin cyanidin-3-O-glucoside in the presence of MgATP but not the aglycones cyanidin and epicatechin. Inhibitor studies demonstrate that TT12 acts in vitro as a cyanidin-3-O-glucoside/H(+)-antiporter. TT12 does not transport glycosylated flavonols and procyanidin dimers, and a direct transport activity for catechin-3-O-glucoside, a glucosylated flavan-3-ol, was not detectable. However, catechin-3-O-glucoside inhibited TT12-mediated transport of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside in a dose-dependent manner, while flavan-3-ol aglycones and glycosylated flavonols had no effect on anthocyanin transport. It is proposed that TT12 transports glycosylated flavan-3-ols in vivo. Mutant banyuls (ban) seeds accumulate anthocyanins instead of proanthocyanidins, yet the ban tt12 double mutant exhibits reduced anthocyanin accumulation, which supports the transport data suggesting that TT12 mediates anthocyanin transport in vitro.
Figures
References
-
- Abrahams, S., Lee, E., Walker, A.R., Tanner, G.J., Larkin, P.J., and Ashton, A.R. (2003). The Arabidopsis TDS4 gene encodes leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase (LDOX) and is essential for proanthocyanidin synthesis and vacuole development. Plant J. 35 624–636. - PubMed
-
- Albert, S., Delseny, M., and Devic, M. (1997). BANYULS, a novel negative regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis in the Arabidopsis seed coat. Plant J. 11 289–299. - PubMed
-
- Baxter, I.R., Young, J.C., Armstrong, G., Foster, N., Bogenschutz, N., Cordova, T., Peer, W.A., Hazen, S.P., Murphy, A.S., and Harper, J.F. (2005). A plasma membrane H+-ATPase is required for the formation of proanthocyanidins in the seed coat endothelium of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102 2649–2654. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown, M.H., Paulsen, I.T., and Skurray, R.A. (1999). The multidrug efflux protein NorM is a prototype of a new family of transporters. Mol. Microbiol. 31 394–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

