Isolated imprinting mutation of the DLK1/GTL2 locus associated with a clinical presentation of maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 14
- PMID: 17601927
- PMCID: PMC2597958
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2007.050807
Isolated imprinting mutation of the DLK1/GTL2 locus associated with a clinical presentation of maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 14
Abstract
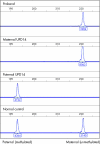
The clinical phenotypes of maternal and paternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 14 (UPD14) are attributed to dysregulation of imprinted genes. A large candidate locus exists within 14q32, under the regulation of a paternally methylated intergenic differentially methylated region (IG-DMR). We present a patient with clinical features of maternal UPD14, including growth retardation, hypotonia, scoliosis, small hands and feet, and advanced puberty, who had loss of methylation of the IG-DMR with no evidence of maternal UPD14. This case provides support for the hypothesis that the maternal UPD14 phenotype is due to aberrant gene expression within the imprinted domain at 14q32.
References
-
- Sutton V R, Shaffer L G. Search for imprinted regions on chromosome 14: Comparison of maternal and paternal UPD cases with cases of chromosome 14 deletion. Am J Med Genet 200093A381–387. - PubMed
-
- Coveler K J, Yang S P, Sutton V R, Milstein J M, Wu Y Q, Knox‐Du Bois C, Beischel L S, Johnson J P, Shaffer L G. A case of segmental paternal isodisomy of chromosome 14. Hum Genet 2002110251–256. - PubMed
-
- Kagami M, Nishimura G, Okuyama T, Hayashidani M, Takeuchi T, Tanaka S, Ishino F, Kurosawa K, Ogata T. Segmental and full paternal isodisomy for chromosome 14 in three patients: Narrowing the critical region and implication for the clinical features. Am J Med Genet 2005138A127–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases