RNA-based regulation of genes of tryptophan synthesis and degradation, in bacteria
- PMID: 17601995
- PMCID: PMC1924887
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.620507
RNA-based regulation of genes of tryptophan synthesis and degradation, in bacteria
Abstract
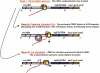
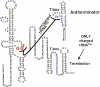
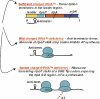
We are now aware that RNA-based regulatory mechanisms are commonly used to control gene expression in many organisms. These mechanisms offer the opportunity to exploit relatively short, unique RNA sequences, in altering transcription, translation, and/or mRNA stability, in response to the presence of a small or large signal molecule. The ability of an RNA segment to fold and form alternative hairpin secondary structures -- each dedicated to a different regulatory function -- permits selection of specific sequences that can affect transcription and/or translation. In the present paper I will focus on our current understanding of the RNA-based regulatory mechanisms used by Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis in controlling expression of the tryptophan biosynthetic operon. The regulatory mechanisms they use for this purpose differ, suggesting that these organisms, or their ancestors, adopted different strategies during their evolution. I will also describe the RNA-based mechanism used by E. coli in regulating expression of its operon responsible for tryptophan degradation, the tryptophanase operon.
Figures















References
-
- Antson, A.A., Dodson, E.J., Greaves, R.B., Chen, X.-P., Gollnick, P. Structure of the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein, TRAP, bound to RNA. Nature. 1999;401:235–242. - PubMed
-
- Anyanful, A., Dolan-Livengood, J.M., Lewis, T., Sheth, S., DeZalia, M.N., Sherman, M.A., Kalman, L.V., Benian, G.M., Kalman, D. Paralysis and killing of Caenorhabditis elegans by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli requires the bacterial tryptophanase. Mol. Microbiol. 2005;57:988–1007. - PubMed
-
- Babitzke, P. Regulation of transcription attenuation and translation initiation by allosteric control of an RNA-binding protein: The Bacillus subtilis TRAP protein. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004;7:132–139. - PubMed
-
- Babitzke, P., Stults, J.T., Shire, S.J., Yanofsky, C. TRAP, the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein of Bacillus subtilis, is a multisubunit complex that appears to recognize G/UAG repeats in trpEDCFBA and trpG transcripts. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:16597–16604. - PubMed
-
- Chen, G.N., Yanofsky, C. Features of a leader peptide coding region that regulate translation initiation for the anti-TRAP protein of Bacillus subtilis . Mol. Cell. 2004;13:703–711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
