Genetic exchange across a species boundary in the archaeal genus ferroplasma
- PMID: 17603112
- PMCID: PMC2013692
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.072892
Genetic exchange across a species boundary in the archaeal genus ferroplasma
Abstract
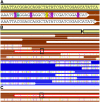
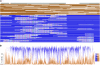
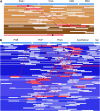
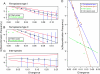
Speciation as the result of barriers to genetic exchange is the foundation for the general biological species concept. However, the relevance of genetic exchange for defining microbial species is uncertain. In fact, the extent to which microbial populations comprise discrete clusters of evolutionarily related organisms is generally unclear. Metagenomic data from an acidophilic microbial community enabled a genomewide, comprehensive investigation of variation in individuals from two coexisting natural archaeal populations. Individuals are clustered into species-like groups in which cohesion appears to be maintained by homologous recombination. We quantified the dependence of recombination frequency on sequence similarity genomewide and found a decline in recombination with increasing evolutionary distance. Both inter- and intralineage recombination frequencies have a log-linear dependence on sequence divergence. In the declining phase of interspecies genetic exchange, recombination events cluster near the origin of replication and are localized by tRNAs and short regions of unusually high sequence similarity. The breakdown of genetic exchange with increasing sequence divergence could contribute to, or explain, the establishment and preservation of the observed population clusters in a manner consistent with the biological species concept.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Searching for species in haloarchaea.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Aug 28;104(35):14092-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706358104. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17715057 Free PMC article.
-
Genome dynamics in a natural archaeal population.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 6;104(6):1883-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604851104. Epub 2007 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17267615 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous recombination in Agrobacterium: potential implications for the genomic species concept in bacteria.Mol Biol Evol. 2009 Jan;26(1):167-76. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn236. Epub 2008 Oct 20. Mol Biol Evol. 2009. PMID: 18936442
-
The interplay of homologous recombination and horizontal gene transfer in bacterial speciation.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;532:29-53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-853-9_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19271178 Review.
-
Cuniculiplasmataceae, their ecogenomic and metabolic patterns, and interactions with 'ARMAN'.Extremophiles. 2019 Jan;23(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s00792-018-1071-2. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Extremophiles. 2019. PMID: 30499003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Steady at the wheel: conservative sex and the benefits of bacterial transformation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Oct 19;371(1706):20150528. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0528. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27619692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bambus 2: scaffolding metagenomes.Bioinformatics. 2011 Nov 1;27(21):2964-71. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr520. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21926123 Free PMC article.
-
Population genomics of early events in the ecological differentiation of bacteria.Science. 2012 Apr 6;336(6077):48-51. doi: 10.1126/science.1218198. Science. 2012. PMID: 22491847 Free PMC article.
-
Functionally relevant diversity of closely related Nitrospira in activated sludge.ISME J. 2015 Mar;9(3):643-55. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.156. Epub 2014 Aug 22. ISME J. 2015. PMID: 25148481 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions in the microbiome: communities of organisms and communities of genes.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014 Jan;38(1):90-118. doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12035. Epub 2013 Aug 28. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 23909933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Meyers and D. J. Lipman, 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bapteste, E., Y. Boucher, J. Leigh and W. F. Doolittle, 2004. Phylogenetic reconstruction and lateral gene transfer. Trends Microbiol. 12: 406–411. - PubMed
-
- Cohan, F. M., 1994. a Genetic exchange and evolutionary divergence in prokaryotes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 9: 175–180. - PubMed
-
- Cohan, F. M., 1994. b The effects of rare but promiscuous genetic exchange on evolutionary divergence in prokaryotes. Am. Nat. 143: 965–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

